Figure 1.
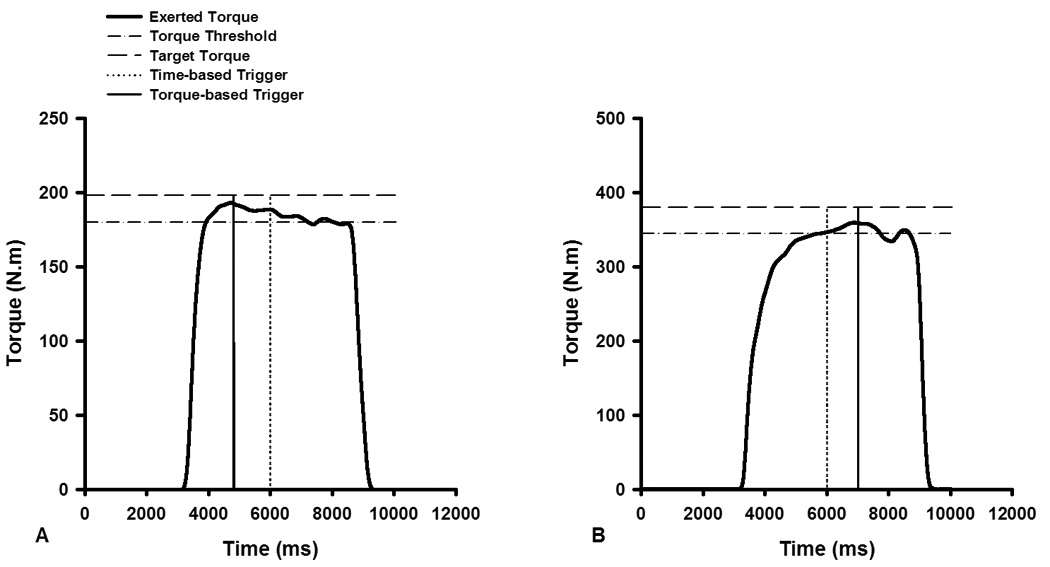
Two representative examples that demonstrate the precision of automated torque-based stimulator triggering in delivering stimuli near-peak torque. The first example (A) is from a female subject, and the second (B) is from a male subject. The torque threshold line represents the torque required to initiate the automated stimulator triggering process. The magnitude of this threshold was set using the peak torque values obtained during preceding MVIC trials. The target torque line established a target that the subjects were instructed to attempt to surpass by as much as possible during their MVIC trials. This was set 10% above the threshold torque value. With the torque-based triggering method (solid vertical lines) a stimulator was triggered when the torque exerted by the subject exceeded the torque threshold and subsequently dropped by 1 N·m. With the conventional time-based triggering method (broken vertical lines) the stimulator was triggered approximately 3 seconds after the onset of contraction. Note that in both examples the torque-based approach triggered the stimulator very close to peak torque, whereas the automated time-based approach triggered the stimulator after peak torque in (A) and before peak torque in (B).
