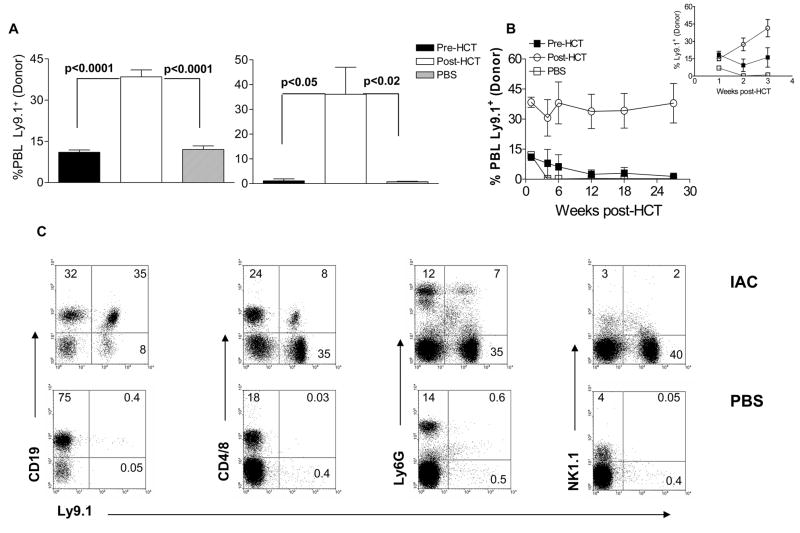
Fig. 4. Administration of IAC post-HCT enhances early and stable long-term peripheral donor (Ly9.1+) chimerism.
B6 mice were sublethally irradiated (5.5 Gy TBI) and injected with IAC pre-HCT (days −5 and −3) or post-HCT (days +3 and +5). Recipient mice received 4 × 106 BALB. B TCD-BM (day 0). Peripheral donor cell (Ly9.1+) frequency was assessed by staining recipient PBL with Ly9.1 at 1 week (A, left) and 27 weeks (A, right) post-HCT. No lethality was observed in any group in this experiment. (B) Kinetics of donor chimerism in the BALB. B → B6 experiment described in 4A following RIC, HCT and pre-HCT or post-HCT IAC administration. Inset represents the rapid increase in donor chimerism levels in IAC infused recipients during the initial 3 weeks post-HCT. (C) Representative dot plots of recipient PBL stained for Ly9.1, CD19, CD4/CD8 and NK1.1 gated on mononuclear cells and Ly6G gated on total donor cells in IAC-treated (top panels) or PBS-treated (bottom panels) control hosts. Data represent dot plots from individual B6 animals 21 weeks post-HCT with BALB. B TCD-BM as described above. Experiments presented above reflect 4 independent experiments (n = 3 – 7 mice/group; results = % donor cells ± SEM). The results demonstrate the presence of multi-lineage donor chimerism at >5 months post-transplant.