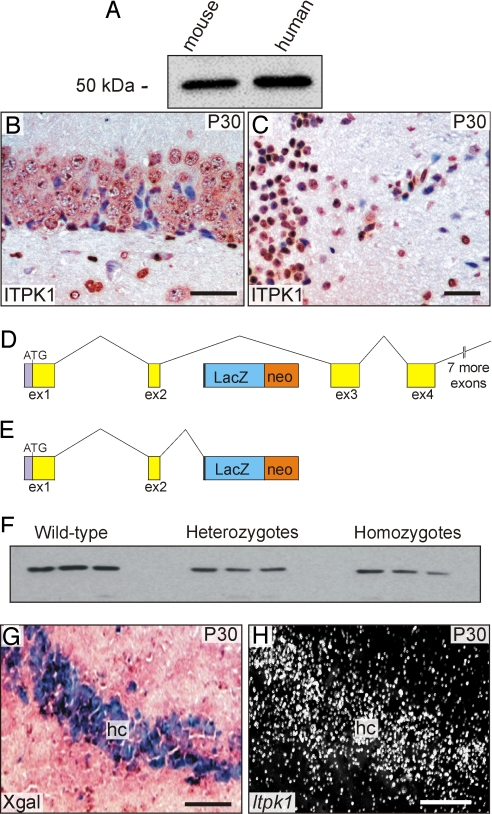
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the ITPK1 antibody and ITPK1 protein levels in mice homozygous for the Itpk1–βgal gene trap allele. (A) Western blot analysis of soluble extracts from cadaveric human and mouse brain (6 μg protein/lane). (B and C) Immunoperoxidase staining of wild-type mouse brain showing ITPK1 immunoreactivity in hippocampal (B) and brainstem (C) neurons. (Scale bar = 30 μm.) (D and E) Diagram of the gene trap allele. Alternative mRNA splicing of the gene trap allele produces both a full-length wild-type transcript (D) and Itpk1–βgal fusion transcript (E). (F) Western blot analysis of ITPK1 protein in soluble brain extracts (2.5 μg protein/lane) from wild-type mice and mice either heterozygous or homozygous for the gene trap allele. (G and H) Correlation of Xgal staining and Itpk1 mRNA expression in a mouse heterozygous for the Itpk1–βgal allele. Adjacent cryosections of hippocampus (hc) were subjected to Xgal staining (G) or in situ hybridization for Itpk1 mRNA (H; dark-field microscopy). (Scale bar = 50 μm.)