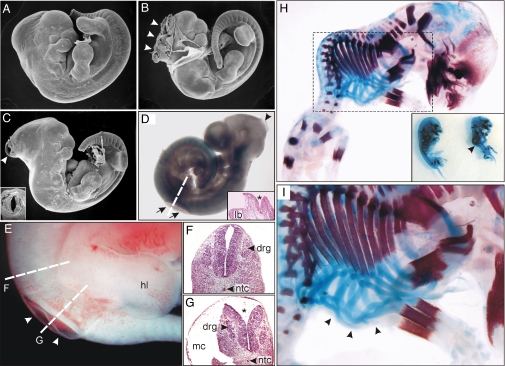
Fig. 3.
NTDs and axial skeleton malformations in mouse embryos homozygous for the Itpk1–βgal gene trap allele. (A–C) Scanning electron micrographs of a normal-appearing E11.5 mouse (A) and 2 littermates (B and C) with varying degrees of exencephaly (arrowheads). The inset in panel C shows another view of the open neural tube. (D) Xgal-stained E10.5 mouse with both exencephaly (arrowhead) and spina bifida (arrows). The dashed line indicates the orientation of the tissue section shown in the inset. The asterisk highlights the open neural tube. (E) Nascent myelomeningocele (arrowheads) in an E11.5 mouse. (F and G) Dashed lines indicate the orientation of tissue sections through the intact neural tube (F) and open neural tube (G, asterisk). (H and I) E14.5 mouse skeletons stained with alcian blue and alizarin red to visualize cartilage and bone. The inset in panel H shows 2 littermates, one of which has kyphoscoliosis (arrowhead). Higher-magnification views of this embryo are shown in panels H and I. Note the presence of malformed ribs (arrowheads in I). Abbreviations: drg, dorsal root ganglia; hl, hind limb; lb, limb bud; mc, myelocele; ntc, notochord.