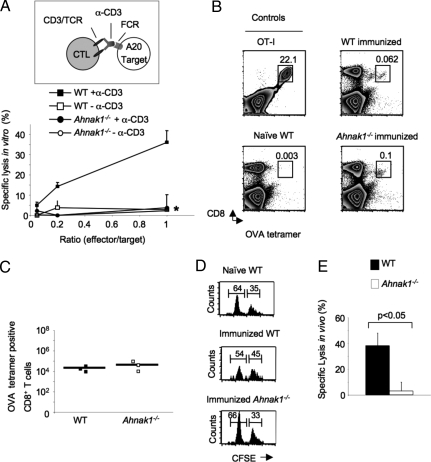
Fig. 2.
Ahnak1−/− CTLs show deficient cytolytic activity in vitro and in vivo. (A) Calcein-AM-loaded A20 were used as targets in the calcein-AM retention CTL assay, with wild-type or Ahnak1−/− CTLs at the noted effector/target ratios and redirected with anti-CD3. Results shown are mean (SD) for 3 individual mice tested per group. We obtained similar results from 2 similar independent experiments. There is a statistically significant difference between wild-type and Ahnak1−/− CTL killing (*, P < 0.05). (B and C) Wild-type dendritic cells, pulsed with H-2Kb-binding SIINFEKL peptide (OVA), were transferred into wild-type and Ahnak1−/− mice. Splenocytes were analyzed for CTL expansion in vivo by H-2kb/OVA257–264 (SIINFEKL) peptide tetramer staining 7 days later. A representative mouse is shown in B. An OT-I mouse is shown as positive control for the tetramer staining, and a naive wild-type mouse is shown as negative control. (C) An average absolute cell number was calculated for 3 individual mice. (D and E) Wild-type and Ahnak1−/− mice were immunized as in B. After 7 days, we co-transferred SIINFEKL peptide (OVA)-loaded CFSE-low-labeled (0.5 μM) mixed with unloaded CFSE-high (5 μM) target wild-type splenocytes. Splenocytes were harvested 3 h later and were analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative naive unimmunized wild-type control mice, immunized wild-type mice, and Ahnak1−/− mice are shown in D. The left and the right peaks shown in the histogram represent the peptide-loaded and unloaded target cells, respectively. Specific lysis was calculated from the ratio between peptide-loaded and unloaded target cells in unimmunized wild-type control and immunized wild-type or Ahnak1−/− mice. An average of 7 mice from each group is shown in E. Significant differences were found between wild-type and Ahnak1−/− mice (P < 0.05).