Figure 3.
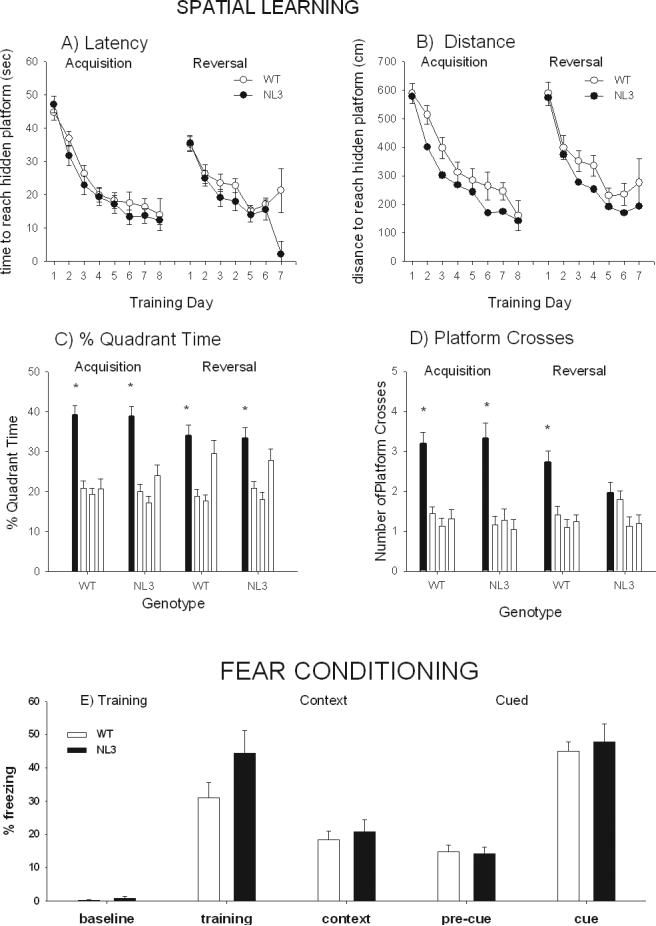
Morris water maze spatial learning and reversal, and contextual and cued fear conditioning measures of cognitive abilities in WT and NL3 knockin mice. A) WT and NL3 displayed similar latencies to locate the hidden platform for both acquisition and reversal of the Morris spatial navigation task. B) NL3 mice swam a shorter distance to find the hidden platform during acquisition but there was no genotype difference in distance swam during reversal. C) Both WT and NL3 spent more time in the previously trained quadrant (black bars) than the other three quadrants (white bars) during the probe trial following the initial acquisition phase. Both WT and NL3 spent more time in the previously trained quadrant than the left and right quadrants, but not the opposite quadrant, during the probe trial following the reversal phase. D) Both WT and NL3 crossed the platform in the previously trained quadrant (black bars) significantly more than the platform locations in other three quadrants (white bars) during the probe trial following the acquisition phase. WT crossed the platform in the previously trained quadrant (black bars) significantly more than the platform locations in other three quadrants (white bars) during the probe trial following the acquisition phase, but NL3 crossed the platform in the trained quadrant more than the the corresponding location in the quadrant to the right, but not the left and opposite locations, during the probe trial following the reversal phase. N = 31 WT, N = 25 NL3. E) Contextual and cued fear conditioning. WT and NL3 did not differ in freezing, a species-specific fear responses measured as the amount of time spent immobile, before training and following training. WT and NL3 did not differ in freezing to the identical context 24 h after training. WT and NL3 did not differ in freezing to a novel context 48 h after training, either in the absence (pre-CS) or presence of the conditioned auditory cue. N = 38 WT, N = 24 NL3.
