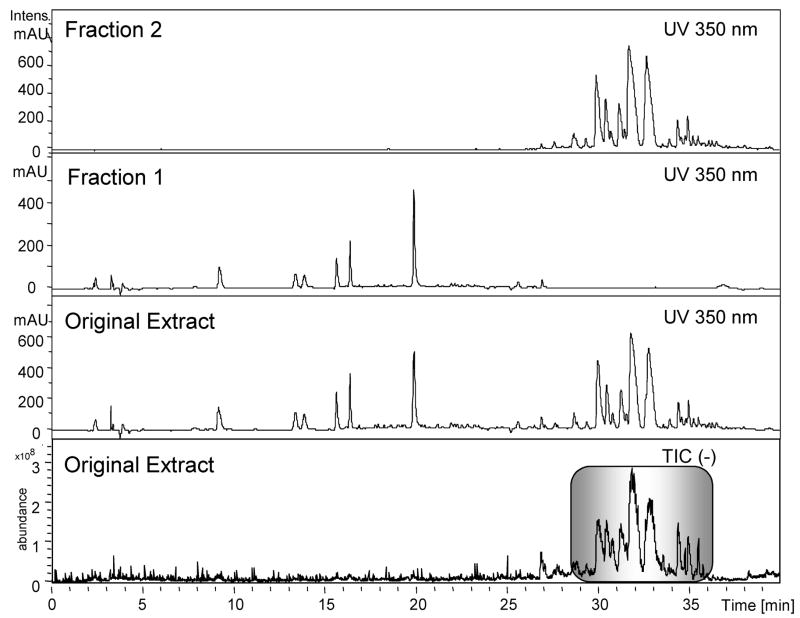
Figure 3.
Semipreparative HPLC separation of H. gentianoides methanol extract. A methanol extract was subjected to semipreparative HPLC and two fractions collected, dividing the more lipophilic constituents (fraction 2) from the more polar constituents, rich in flavonoids such as quercetin (fraction 1), as shown in this analytical LC-UV-MS data. The total ion chromatograph (TIC) from the liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–mass spectrum analysis shows that the unknown lipophilic compounds (highlighted in the box) based on TIC peak area, comprise approximately 79% of the methanol extract’s mass, accounting for 2% of the plant fresh weight. This high abundance will facilitate purification of enough material for bioactivity-guided fractionation starting with only tens of grams of dry plant material.