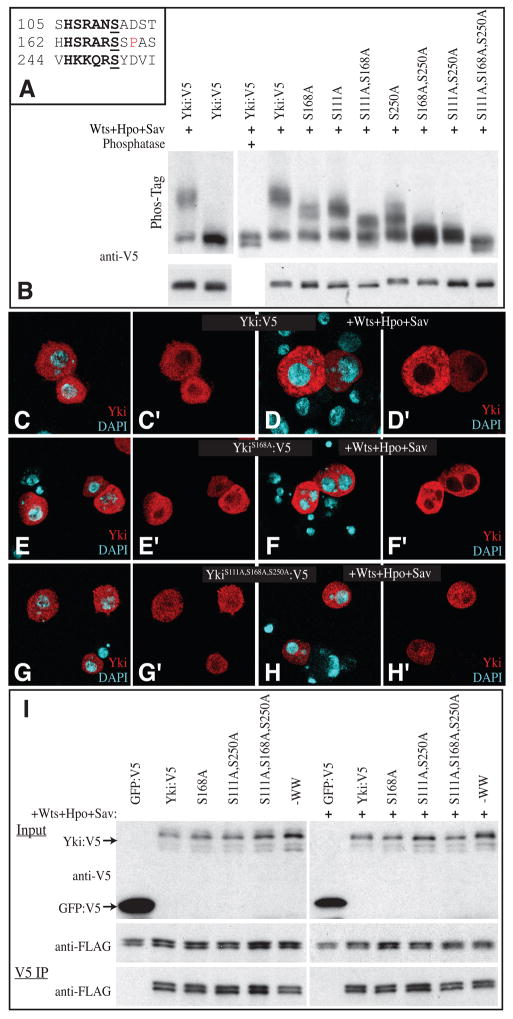
Figure 1. Phosphorylation of Yki Ser111 and Ser250 in S2 cells.
(A) Amino acid sequence surrounding the three consensus Wts phosphorylation sites within Yki. The consensus sequence motif (HX(R/H/K)XX(S/T)) is in bold, the phosphorylation site is underlined, and a Pro that forms part of a 14-3-3 binding motifis in red. (B) Western blots (anti-V5) on lysates of S2 cells co-transfected to express Yki:V5, or a phosphorylation site mutant isoform, and, where indicated, Wts, Hpo and Sav to promote Yki phosphorylation. Upper panels show Phos-Tag gels (50 μM Phos-Tag); lower panels show 4–15% gradient gels. Phosphorylation results in mobility shifts proportional to the extent of phosphorylation, which are reversed by phosphatase treatment. (C–H) S2 cells, stained for Yki (red) and nuclei (DAPI, cyan) in the presence (D, F and H) or absence (C, E and G) of exogenous Hpo, Sav and Wts. Panels marked ‘ show individual channels of the stain on the left. (C, D) Wild type Yki:V5; (E–F) YkiS168A:V5; (G–H) YkiS111A,S168A,S250A:V5. (I) Western blots (4–15% gel) of samples from S2 cells co-transfected to express the indicated proteins. Top (Yki:V5 and GFP:V5) and middle (Sd:FLAG) panels shows input, bottom panel (Sd:FLAG) shows blot on material precipitated by anti-V5 beads. Faint bands detected below Yki:V5 in top panel are the result of incomplete stripping-off of Sd:FLAG.