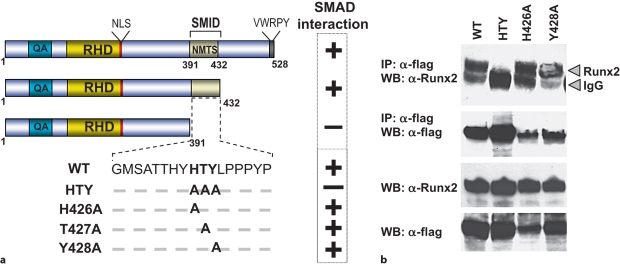
Fig. 1.
Three residues in the SMID of RUNX2 are required for formation of the RUNX2-SMAD complex. a Schematic illustration of various conserved region and C-terminal deletion as well as SMID mutant RUNX2 protein. QA = Polyglutamic acid and alanine stretch; RHD = DNA-binding runt homology domain; NLS = nuclear localization signal. SMID resides between amino acids 391 and 432. BMP2- or TGF-β-responsive SMAD (Smad1, 2 and 3) interactions with key RUNX2 point mutants determined by coimmunoprecipitation studies are indicated. b HeLa cells were cotransfected with 5 μg of Smad1 and indicated Runx2 expression vectors and cultured in the presence of 100 ng/ml of BMP2. Only mutation of all 3 amino acids resulted in loss of RUNX2-SMAD interaction. Lower panels show expression of RUNX2 and SMAD proteins in the input sample. IP = Immunoprecipitation; WB = Western blotting.