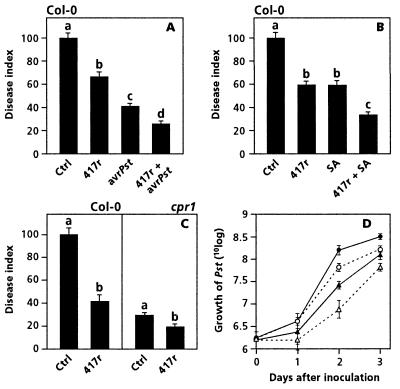
Figure 1.
Induced protection against Pst in Arabidopsis plants expressing ISR, SAR, or both types of induced resistance. ISR was induced by growing the plants in soil containing WCS417r (417r) at 5 × 107 cfu/g. SAR was induced in wild-type Col-0 plants by preinfecting three leaves per plant with avirulent Pst(avrRpt2) (avrPst) at 107 cfu/ml (A), or by exogenous application of 1 mM SA (B) 3 days before challenge inoculation. Mutant cpr1 constitutively expressed SAR (C). The disease index is the mean ± SE (n = 20 plants) of the proportion of leaves with symptoms per plant relative to that of control-treated (Ctrl) Col-0 plants (set at 100%), 4 days after challenge with virulent Pst. The absolute proportions of diseased leaves of the control-treated Col-0 plants depicted in A, B, and C were 55%, 52, and 71%, respectively. Within each frame, different letters indicate statistically significant differences between treatments (Fischer's Least Significant Differences test; α = 0.05). Corresponding bacterial growth data are given in Table 1. The data presented are from representative experiments that were repeated at least twice with similar results. In D, growth curves of Pst in Col-0 plants expressing ISR and in cpr1 plants expressing either SAR or both SAR and ISR. Values presented are average numbers (±SE) of cfu/g fresh weight, each from five whole shoots harvested 0, 1, 2, or 3 days after challenge with Pst. For experimental details see text and Table 1 legend. The additive effect on inhibition of pathogen growth in the combination treatment was statistically significant at all time points tested (Fisher's Least Significant Differences test; α = 0.05). Circles, Col-0 plants; triangles, cpr1 plants; solid lines with closed symbols, control treatment; and dotted lines with open symbols, WCS417r treatment.