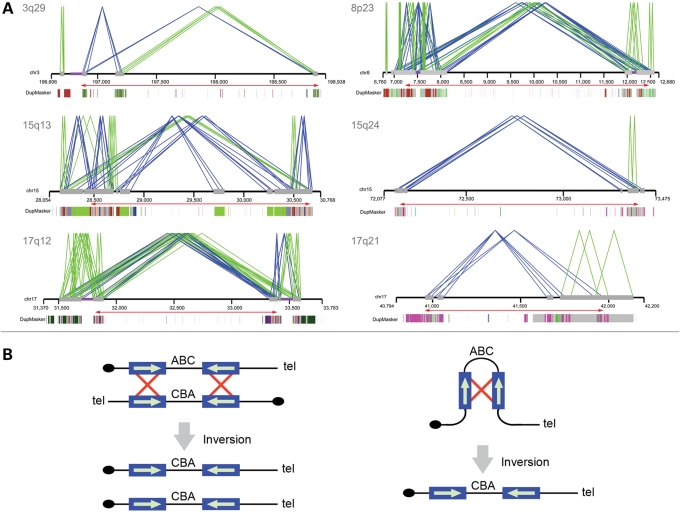
Figure 1.
Duplication architecture of inversion breakpoint regions. (A) Paralogy between large (≥10 kb), highly identical (≥95%) segmental duplications (gray bars) is shown. Direct (green lines) or inverted (blue lines) orientations of pairwise alignments of segmental duplications are indicated. A relaxed threshold (size ≥5 kbp and sequence identity ≥90%) was applied for the 15q24 inversion. The underlying ancestral duplication (duplicon) (24) composition of each duplication as determined by DupMasker (45) is represented as color-coded blocks. Red arrows show the extent of the inverted region. (B) Interchromosomal, intrachromosomal or intrachromatid non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) between inverted repeats causes inversion of the intervening sequence. Repeat sequences are indicated as blue boxes, with their orientation indicated by green arrows and recombination is shown by red crosses. Adapted in part from Sharp et al. (48).