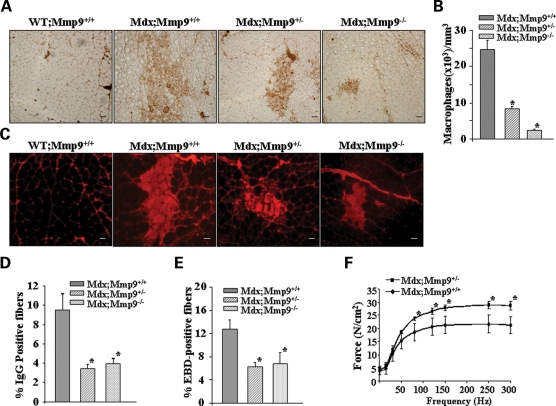
Figure 4.
Genetic ablation of MMP-9 attenuates muscle pathology in mdx mice. (A) Representative photomicrographs of gastrocnemius muscle sections immunostained for F4/80 antigen suggest that the accumulation of macrophages in skeletal muscle is decreased in mdx;Mmp9+/− and mdx;Mmp9−/− mice compared with littermate mdx/Mmp9+/+ mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Quantification of F4/80 positive cells revealed significantly (*P < 0.001) reduced concentration of F4/80 stained cells in mdx;Mmp9+/− (n = 4) and mdx;Mmp9−/− (n=5) compared with mdx;Mmp9+/+ (n = 3) mice. (C) Gastrocnemius muscle cross-sections from 7- to 8-week mdx;Mmp9+/+, mdx;Mmp9+/− and mdx;Mmp9−/− mice were immunostained with Cy3-labelled goat anti-mouse IgG to detect necrotic fibers. Scale bar: 50 µm. (D) Percentage of IgG positive (filled with red color) fibers was significantly (*P < 0.05) lower in mdx;Mmp9+/− (n = 5) and mdx;Mmp9−/− (n = 6) mice compared with littermate mdx;Mmp9+/+ (n = 4) mice. (E) Percentage of EBD-positive cells were also found to be decreased in gastrocnemius muscle of mdx;Mmp9+/− or mdx;Mmp9−/− compared with littermate mdx;Mmp9+/+ mice. *P < 0.05, values significantly different from mdx;Mmp9+/+ mice. (F) Force–frequency curves. Data presented here are the average force produced by soleus muscle of mdx;Mmp9+/+ (n = 4) and mdx;Mmp9+/− mice (n = 4). *P < 0.05, values significantly different from corresponding mdx;Mmp9+/+ mice at indicated frequency.