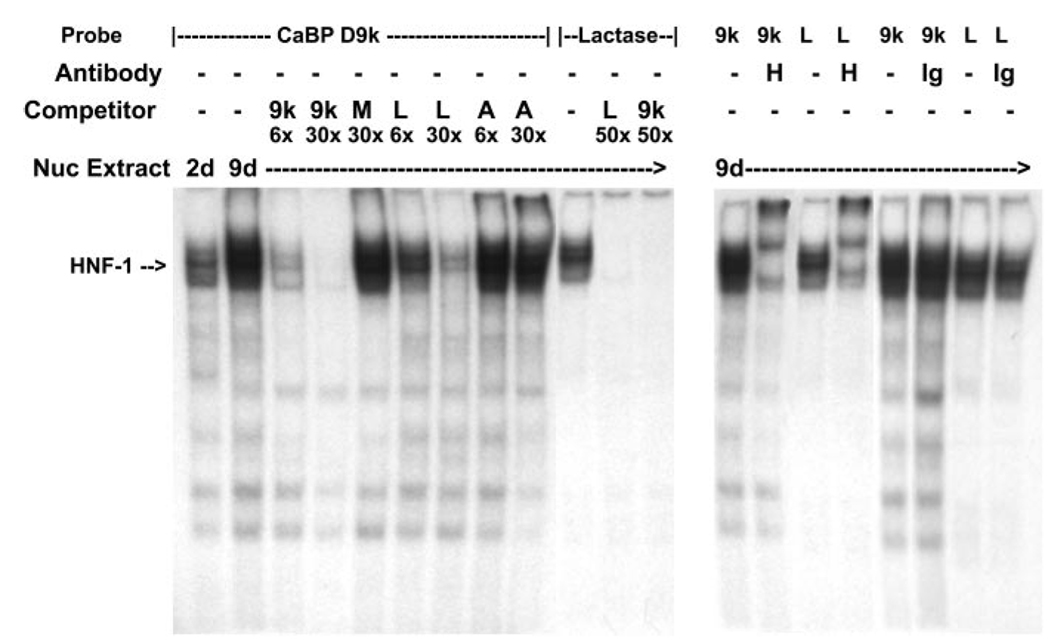
Fig. 5.
EMSA analysis of HNF-1 binding to the distal HNF-1 response element in conserved cluster I of the calbindin D9k promoter. Oligonucleotides containing the putative HNF-1 site from cluster I in the human calbindin D9k promoter (CaBP D9k) or a well-characterized HNF-1 site from the lactase promoter (Lactase) were labeled with [γ-32P]ATP by T4 polynucleotide kinase. Left: competitive gel-shift assay. Nuclear extracts (Nuc Extract; 10 µg) from preconfluent (2 days) or 5-day postconfluent (9 days) TC7 cells were used for each binding reaction. The specific HNF-1α-containing complex is marked with an arrow. Specificity of complex formation was confirmed by competition with a 6-fold (6×) or 30-fold (30×) molar excess of unlabeled probe (9k, CaBP-HNF-1; M, mutated CaBP-HNF-1; L, lactase HNF-1; A, AP2). Specificity of complex formation on the labeled lactase HNF-1 probe was confirmed by competition with a 50-fold molar excess of unlabeled calbindin D9k HNF-1 probe or lactase HNF-1 probe. Right, HNF-1α supershift assay. Nuclear extracts (10 µg) from 9-day cultures of TC7 cells were preincubated with HNF-1α antibody (H) or a goat IgG (Ig) before incubation with 32P-labeled calbindin D9k HNF-1 probe or lactase HNF-1 probe.