Figure 3.
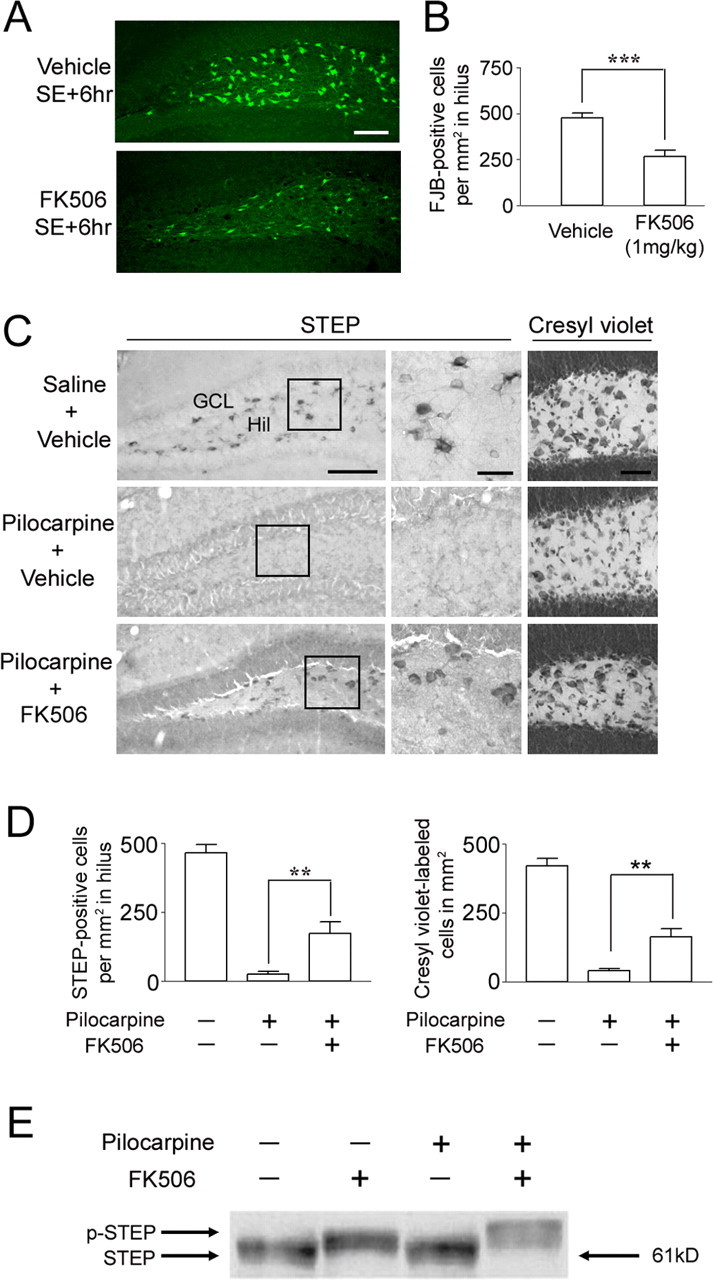
FK506 attenuates SE-induced cell death in the hilus. FK506 (1 mg/kg) or vehicle (20% DMSO in saline) was injected intraperitoneally 15 min after pilocarpine injection. Mice were killed 6 h after SE, and cell death was identified by Fluoro-Jade B staining. A, Representative images reveal Fluoro-Jade B-positive cells in the hilus. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, Cell counts of Fluoro-Jade B (FJB)-positive cells reveal that FK506 significantly reduced SE-induced cell death. ***p < 0.001. C, FK506 conferred lasting protection to STEP-expressing hilar (Hil) interneurons. Representative images of STEP immunolabeling in the dentate gyrus from animals killed 7 d after SE are shown. Note the large number of STEP-positive cells in the hilus of mice given injections of FK506 (bottom). In contrast, in the absence of FK506 treatment, STEP-positive cells were not observed in SE-induced mice (middle). Cresyl violet staining (right) is consistent with STEP immunostaining; FK506 attenuated SE-induced cell loss in the hilus. Scale bars: low-magnification images, 100 μm; high-magnification images, 25 μm. D, Quantitation of STEP- and cresyl violet-positive cells 7 d after pilocarpine-induced SE. **p < 0.01. E, Western blotting was used to detect the active (dephosphorylated) and inactive (phosphorylated) form of STEP (p-STEP). Under both control conditions (lane 1) and after pilocarpine injection (lane 3) (15 min after SE onset), STEP migrated in its lower-molecular-weight (dephosphorylated) active form. After FK506 (1 mg/kg) injection alone (lane 2) or with pilocarpine (lane 4), STEP migrated in its higher-molecular-weight (phosphorylated) inactive form. Error bars indicate SEM.
