Figure 2. Phenotypes associated with Pten heterozygosity require mTORC2.
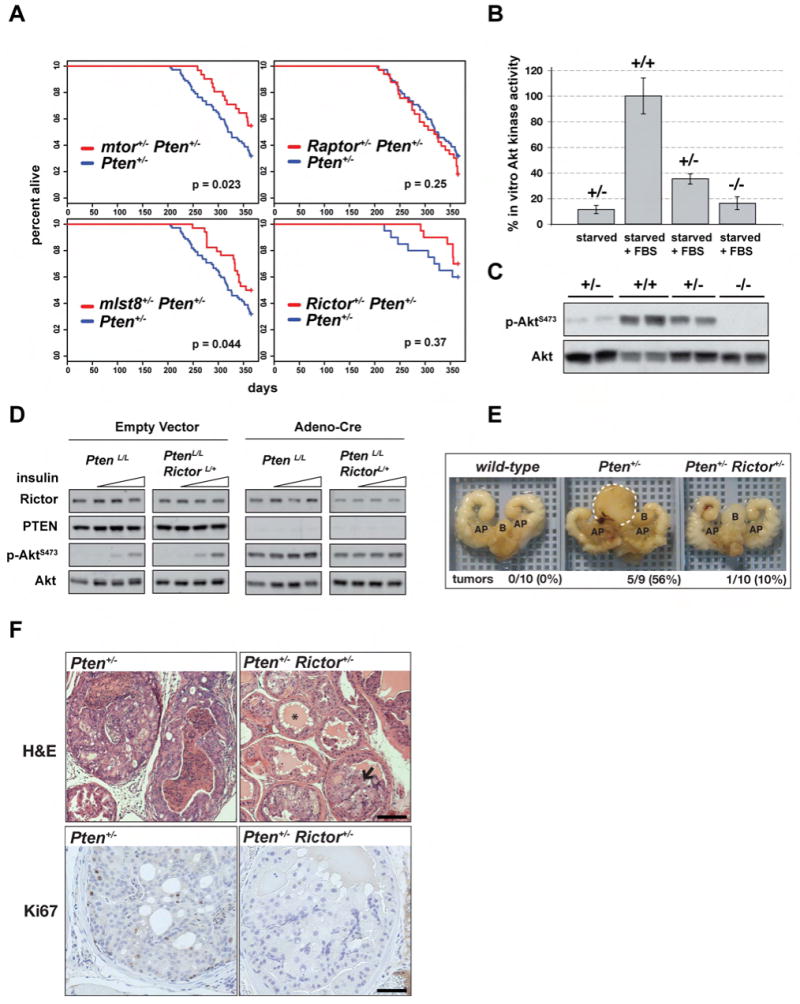
(A) Pten+/- mice lacking one mtor, mlst8, or Rictor gene tend to live longer. Survivability was monitored for 1 year and displayed using Kaplan-Meyer plots. (B-C) Rictor+/- MEFs have reduced Akt activity. (B) Akt was isolated from serum deprived (starved) or stimulated (+FBS) MEFs that were wild-type or deleted for one or both Rictor genes. The ability of immunopurified Akt to incorporate radiolabeled phosphate into a synthetic substrate was measured. Bars indicate standard error. (C) Immunoblot corresponding to (b) showing phospho-AktS473 and total Akt levels. (D) Adeno-Cre was added to MEFs harboring conditional alleles of Pten and Rictor (PtenL/L and PtenL/LRictorL/+) to generate Pten-null MEFs lacking only one Rictor gene. Empty vector was added to generate control cells. Lysates were prepared from serum-deprived cells that were stimulated with 0, 1, 10, or 100nm insulin for 10 minutes and probed with the indicated antibodies. (E-F) Pten+/-Rictor+/- mice are protected against prostate tumor development. (E) GU tracts of wild-type, Pten+/- and Pten+/-Rictor+/- mice that survived to 1 year were dissected and photographed. Bladder (B) and Anterior Prostate (AP) are indicated for orientation. An example of a large tumor associated with a Pten+/- prostate is circled with a white dotted line. (F) Pten+/- and Pten+/-Rictor+/- prostate tissue was sectioned and stained by Hematoxylin & Eosin (top) or labeled with Ki-67 antibody (bottom). Representative images are shown. The star (*) indicates a normal prostate ductule and the arrow points to a ductule containing large hyperplastic cells. Scale bar = 50μm (top) and 25μm (bottom).
