FIGURE 3. Reduction of COBRA1 in breast cancer cells results in elevated transcriptional activation by AR.
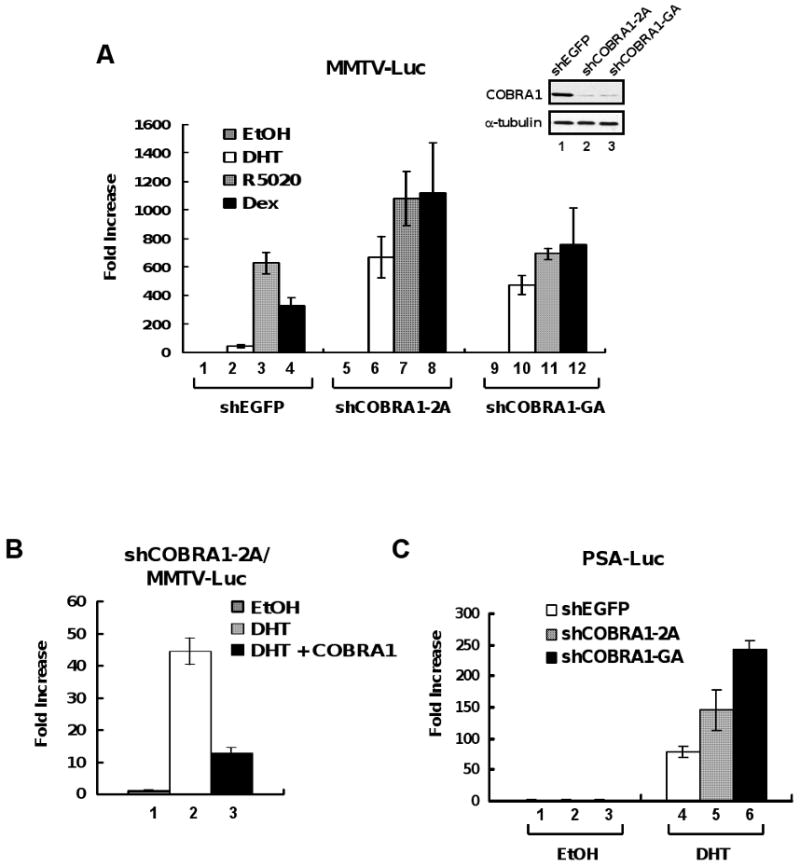
A. The inlet shows an α-COBRA1 immunoblot in T47D-derived cell lines that stably expressed short hairpin RNAs against EGFP control (shEGFP) or COBRA1 (shCOBRA1-2A and shCOBRA1-GA). α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. MMTV-luciferase reporter plasmid was transiently transfected in the control or two COBRA1 knockdown cell lines. The cells were treated with DHT (10 nM; open bars), R5020 (10 nM; shaded bars), or dexamethasone (Dex, 100 nM; solid bars) for 24 hours before harvesting for luciferase assay. Ethanol was used as vehicle. Steroid hormone-dependent transcription was expressed as fold increase over vehicle. B. A COBRA1 silent mutant (COBRA1) that is refractory to shCOBRA1-2A was co-expressed with the MMTV-luciferase reporter plasmid in stable knockdown cells expressing shCOBRA-2A. Transfected cells were treated with DHT (10 nM) for 24 hours before harvesting for luciferase assay. C. DHT (10 nM)–dependent transcription from the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) promoter in the control and two COBRA1 knockdown cells as measured by luciferase assay.
