Figure 1.
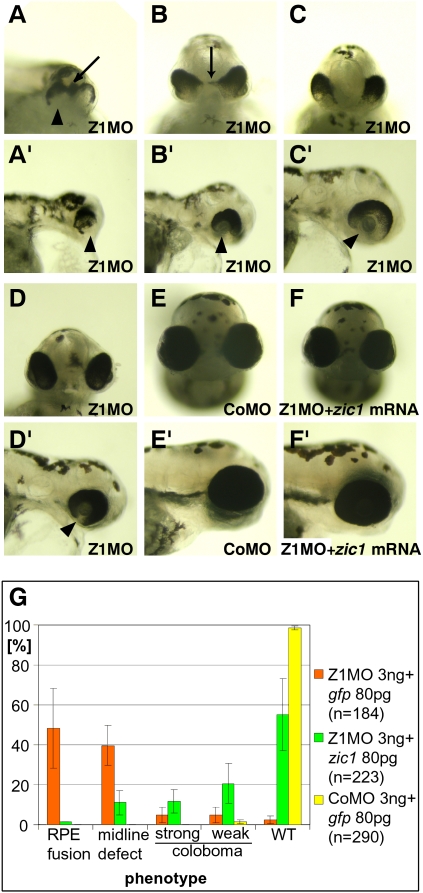
Zic1 LOF elicits defective development of the embryonic midline and the eye at 72 hpf. (A–F) Frontal view. (A′–F′) Lateral view with rostral to the right. (A,A′) Severely affected embryos show dorsal fusion of RPE of both eyes (arrow) indicating disturbed midline development. RPE is missing in the ventral eye (arrowhead). (B,B′) Less severely affected embryos show an expansion of RPE into the optic stalk domain (arrow). Massive coloboma can be observed in the ventral eye (arrowhead). (C,C′) In weakly affected embryos, coloboma is still pronounced (arrow). (D,D′) Morphants with a very weak phenotype show weak but clearly detectable coloboma (arrowhead). (E,E′) Control morpholino-injected embryo. (F,F′) Coinjection of Zic1 morphants with zic1 mRNA rescues the phenotype. (G) Quantification of frequency of described phenotypes and rescue experiment. Most embryos injected with Z1MO show RPE fusion and midline defects, whereas most morphants coinjected with zic1 mRNA show only coloboma or no phenotype. (WT) Wild type.