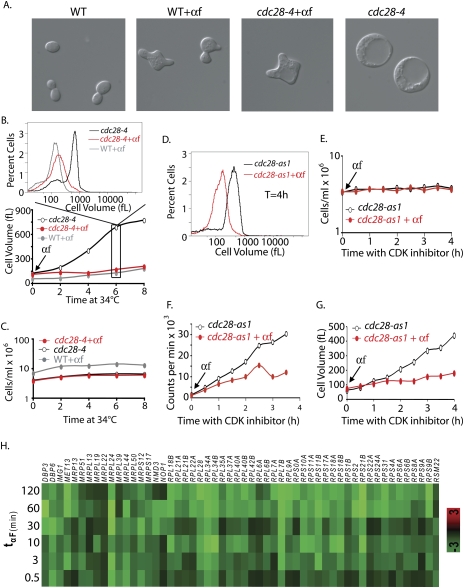
Figure 2.
Polarization limits growth in cdc28-4 mutants. The micrographs in A show wild-type (A2589) and cdc28-4 (A22928) cells at 6 h after the temperature shift with or without α-factor treatment. (B,C) Wild-type (A2589, bar1∷HisG; gray circles) and cdc28-4 bar1∷HisG (A22928) cells were shifted to 34°C and either treated with 20 μg/mL α-factor (black circles) or left untreated (red circles). Modal cell volume (B) and cell number (C) were determined at the indicated times. The cell volume distributions for the 6-h time point are shown above the graph in B. (D–G) cdc28-as1 (A4370) cells were shifted to 30°C and arrested with 5 μM CDK inhibitor, and 35S methionine and 35S cysteine (20 μCi/mL final each) were added. (F) The culture was split and either treated with mating pheromone (20 μg/mL; red circles) or mock-treated (black circles) and 35S incorporation into total protein was determined as described in Materials and Methods. A parallel culture treated identically but with unlabeled amino acids was used to determine cell number (E) and cell volume (G). The cell volume distribution of the two cultures at 4 h after temperature shift is shown in D. (H) Gene expression profile of 54 down-regulated RPs during mating in the wild-type strain (MT1567). Genome-wide gene expression was examined at different time points after pheromone addition. Down-regulated genes were significantly enriched for only one MIPS functional category: RPs (54 genes; P < 1.198e-06). Log2 (treated/untreated) values are indicated for each gene (y-axis) at various times (min) after pheromone addition (x-axis).