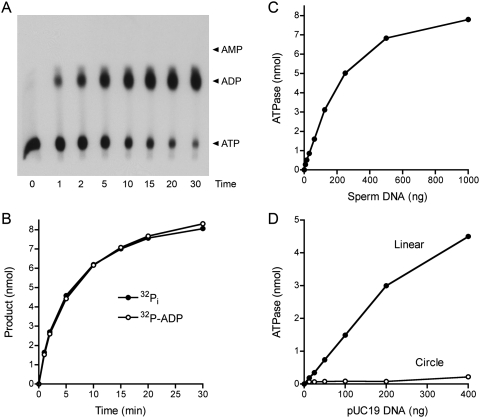
Figure 2.
AdnAB is a DNA-dependent ATPase. (A,B) Reaction mixtures (60 μL) containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM [α32P]ATP or [γ32P]ATP, 1 mM MgCl2, 10 μg of salmon sperm DNA, and AdnAB (60 ng AdnB) were incubated at 37°C. Aliquots (5 μL, containing 5 nmol input ATP) were withdrawn at the times specified and quenched with formic acid. Reaction products were analyzed by PEI-cellulose TLC and visualized by autoradiography. The analysis of products from the reaction containing [α32P]ATP is shown in A, with the positions of cold ATP, ADP, and AMP standards indicated on the right. The extent of conversion of [γ32P]ATP to 32Pi (●) or [α-32P]ATP to [α-32P]ADP (○) is plotted as a function of time in B. (C) DNA dependence of ATP hydrolysis. Reaction mixtures (10 μL) containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM DTT, 1 mM [γ32P]ATP, 1 mM MgCl2, AdnAB (10 ng AdnB), and salmon sperm DNA as specified were incubated for 5 min at 37°C. 32Pi release is plotted as function of the amount of DNA added. (D) ATP hydrolysis requires free DNA ends. Reaction mixtures (10 μL) containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM [γ32P]ATP, 1 mM MgCl2, AdnAB (10 ng AdnB), and either closed circular pUC19 DNA or blunt-ended linear pUC19 DNA (SmaI-digested) were incubated for 5 min at 37°C. 32Pi release is plotted as function of the amount of DNA added.