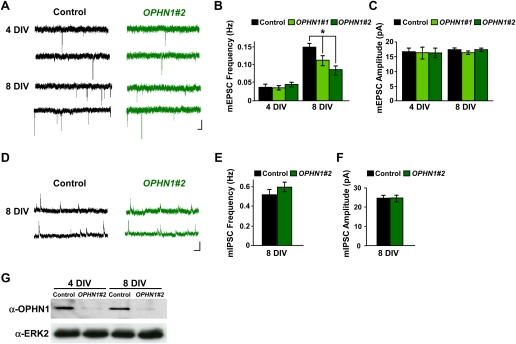
Figure 2.
OPHN1 is critical for normal synaptic maturation. (A) Representative traces of excitatory miniature events recorded at −60 mV from uninfected neurons (control) and neurons expressing OPHN1#2 shRNA at different developmental stages (4 and 8 DIV). Bars, 2 sec and 20 pA. (B,C) Quantification of mEPSC frequency (B) and amplitude (C) for control and OPHN1#1 and OPHN1#2 shRNA-expressing neurons at different developmental stages. (B) Four days in vitro: n = 18 cells for all groups; 8 DIV: control: n = 30 cells; OPHN1#1: n = 21 cells; OPHN1#2: n = 30 cells. (C) Four days in vitro: n = 18 cells for all groups, 8 DIV: control: n = 30 cells; OPHN1#1: n = 21 cells; OPHN1#2: n = 30 cells. (D) Representative traces of inhibitory miniature events recorded at +10 mV from uninfected neurons (control) and neurons expressing OPHN1#2 shRNA at 8 DIV. Bars, 1 sec and 20 pA. (E,F) Quantification of mIPSC frequency (E) and amplitude (F) from control and OPHN1#2 shRNA-expressing neurons at 8 DIV (n = 24 for both groups). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. (*) P < 0.005 by Student's t-test. (G) Immunoblot of extracts prepared from hippocampal neurons 4 and 8 d post-infection with scr#1 (control) or OPHN1#2 shRNA probed with anti-OPHN1 and anti-ERK2 antibody as a loading control.