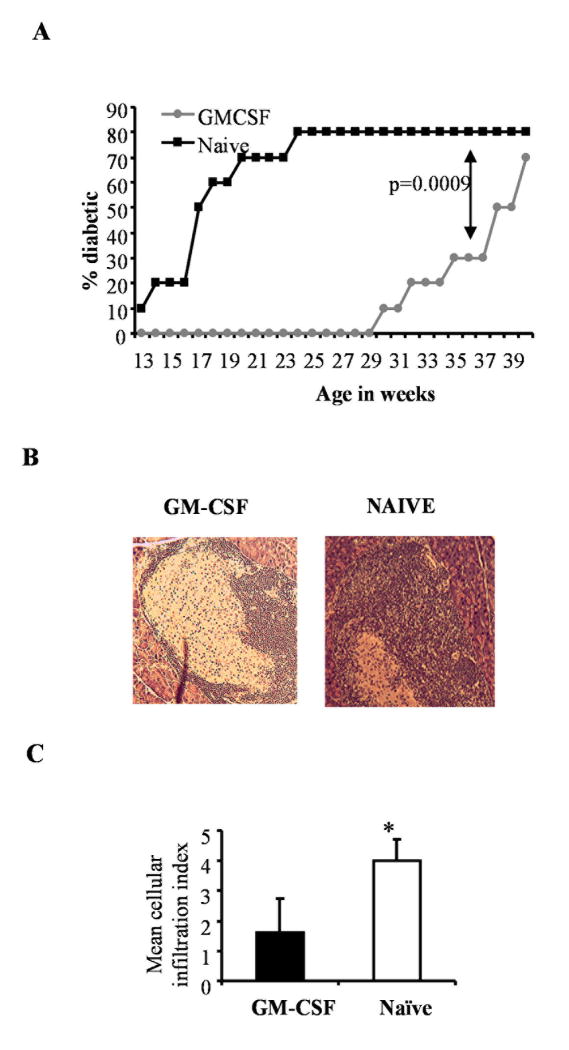
Figure 3. Therapeutic potential of GM-CSF.
Groups of 10 NOD mice were treated with 2μg/mL/mouse of GM-CSF or PBS (naïve) for five consecutive days starting 7, 9, 11, 13, 15 and 19 weeks of age and monitored for T1D. A) Blood glucose levels monitored weekly and the mice were considered diabetic when glucose levels remained above 250 mg/dL for 2 consecutive weeks. Log-rank test was carried out to determine statistical significance. B) Pancreatic sections from a set of mice were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Representative images of islets from GM-CSF-treated and naive animals are shown. C) Stained sections were examined, insulitis was scored in a blinded fashion as described in research design and methods, and the mean±SD of insulitis grades plotted as bar-diagram. * indicates a p value of <0.05.