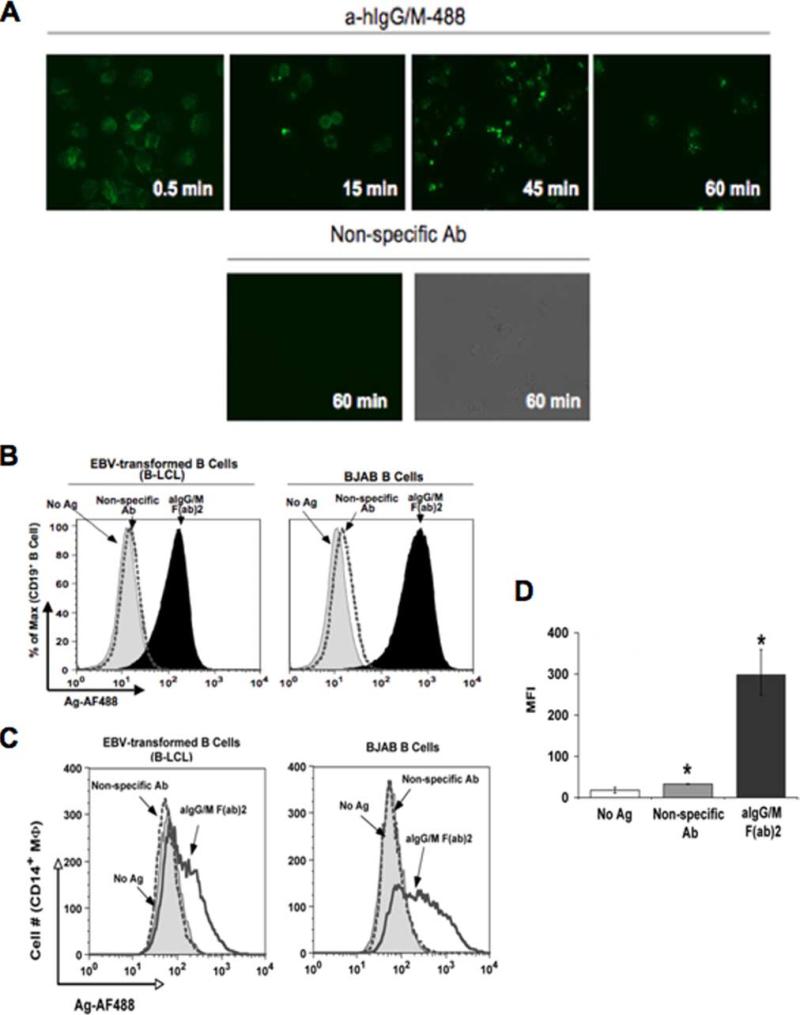
FIGURE 1.
Human B cells acquire and transfer Ag to macrophages. A, Kinetics of Ag uptake by B cells. B-LCLs pulsed with either AF488-congugated anti-human Ig (a-hIgG/M-488; upper panels) or nonspecific Ab (lower panels) for the indicated time points were washed and observed by fluorescence microscopy (×450 original magnification). B, Ag uptake by various B cell lines. B-LCL (left panel) and BJAB (right panel) were pulsed with no Ag (gray-shaded curve), nonspecific Ab (dotted curve), or anti-IgG/M (aIgG/M; filled curve) and stained with anti-CD19 Ab for flow cytometry. C, Various B cell lines transfer Ag to macrophages (MΦ). Human PBMC-derived macrophages were cocultured for 18 h at a 1:2 ratio with B-LCL (left panel) or BJAB (right panel) pulsed with no Ag (gray-shaded curve), nonspecific Ab (dotted curve), or anti-Ig (aIgG/M F(ab)2; open curve). Cells were stained with anti-CD19 and CD14 Abs for flow cytometry. Levels of Ag (AF488) was assessed for the CD19−CD14+-gated population. D, Levels of transferred Ag are significant. MFI values for transferred Ag (AF488) are given for three independent experiments (*, p = 0.0012).