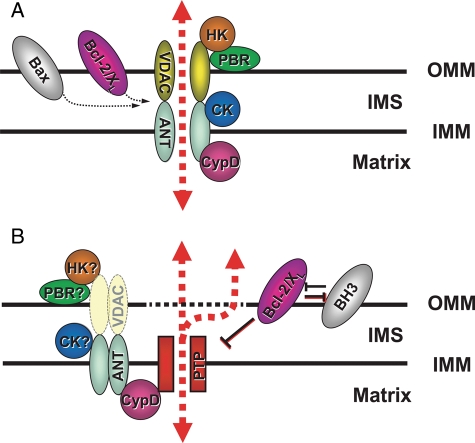
Figure 1.
Proposed mPTP complex architecture: (A) Classical view. The mPTP structure is formed by the VDAC–ANT–CyP-D complex, which is located at the ‘contact sites’. Hexokinase II (HKII), mitochondrial creatine kinase (CK), benzodiazepine receptor (PBR), and Bcl-2-family members (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Bax) are included as putative regulatory components. (B) Current view. The core elements comprising the mPTP itself (denoted ‘PTP’ for permeability transition pore) are presently unidentified, but are probably regulated by the adjacent elements as indicated. Note that VDAC, portrayed as a ‘shadow,’ is no longer seen as an essential pore component or even a regulator based on recent genetic evidence. Question mark symbols signify where important open questions remain as far as the participation as a regulator of the mPTP (see text; modified from Juhaszova et al.9).