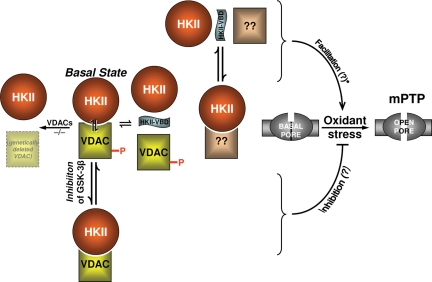
Figure 3.
Regulatory roles of VDAC and HKII. Figure layout scheme is the same as in Figure 2. Middle row of the scheme depicts the basal state of VDACs (WT and genetically deleted) and HKII, and their relationship to the basal state and oxidant stress-induced mPTP. mPTP is similar in WT controls as well as in mitochondria lacking VDACs, thus VDAC is dispensable for mPTP-induction. Top row represents facilitation of the ROS-induced mPTP by HKII-VBD peptide: however, because VDAC is dispensable, it is possible that HKII dissociation from some other site may be relevant. Note that this still does not prove that the HKII dissociation from any site by HKII-VBD peptide is casually related to facilitation of mPTP-induction. Bottom row: GSK-3β inhibition results in VDAC dephosphorylation which has been linked with cell protection,81,83 so it remains possible that VDAC phosphorylation may be involved in mPTP regulation.