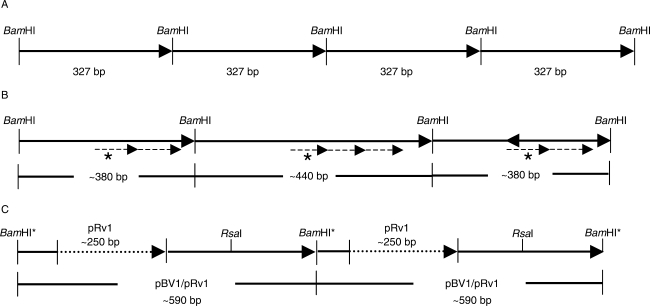
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the structural variations of the pBV1 satellite repeat in the B. vulgaris genome. (A) Tandemly arranged pBV1 monomeres of 327 bp. The BamHI restriction sites define the satellite monomeres according to Schmidt and Metzlaff (1991). (B) Size variations of pBV1 monomeres detected on a B. vulgaris bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC). The monomer length is increased to approx. 380 bp by an internal duplication (dashed arrow) of a 60-bp sequence motif (dashed arrows, labelled with an asterisk). An amplification of the 60-bp motif resulted in a monomer of approx. 440 bp. (C) Interspersion of a pRv1 unit of approx. 250 bp (dotted arrow) into pBV1 monomeres of approx. 340 bp. The combined pBV1/pRv1 unit observed on end-sequenced BACs and plasmid clones is approx. 590 bp in length and contains a unique RsaI restriction site, while the BamHI site is degenerated (indicated by an asterisk).