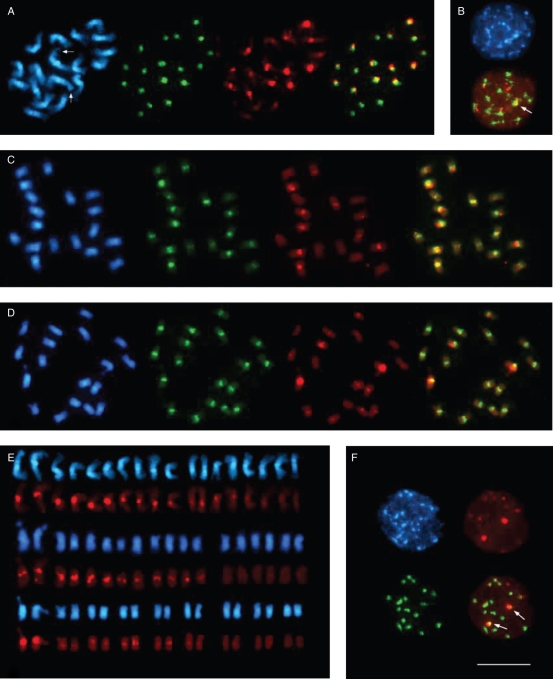
Fig. 5.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization to metaphase and interphase chromosomes of species of the section Beta. In each panel, the DAPI-stained DNA (blue fluorescence) shows the morphology of the chromosomes. The pBV1 hybridization signals are visible as green fluorescent signals, and red fluorescence indicates pRv1 hybridization. Comparison of the signal pattern of pBV1 and pRv1 probes hybridized to metaphase chromosomes of B. vulgaris (A), B. patula (C) and B. macrocarpa (D), indicating a species-specific centromeric localization of both repeat families. The B. vulgaris chromosome pair I is marked by arrows. The right picture in (A), (C) and (D) represents an overlay of the pBV1 and pRv1 hybridization. (B) Centromeric localization of pBV1 and pRv1 is visible as signals on chromocentres of B. vulgaris interphase nuclei. The embedment of pRv1 into areas of pBV1 is highlighted by an arrow in the overlay (bottom). (E) Arrangement of metaphase chromosomes from B. vulgaris (top), B. patula (middle) and B. macrocarpa (bottom) according to the observed signal strength of centromeric pRv1 hybridization. The pair of chromosome I for each species is placed on the left. (F) Centromeric localization of pBV1 and pRv1 signals in the centromeric heterochromatin of B. macrocarpa interphase chromosomes. The distinct cluster of pRv1 adjacent to a pBV1 area is visible as yellow fluorescence (indicated by arrows, bottom right). Scale bar (in F) = 10 µm.