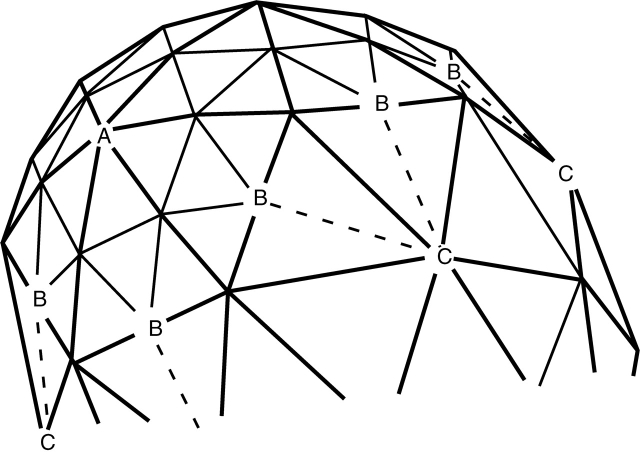
Fig. 3.
Computational representation of the surface, by finite elements. The initial shape (hemispherical or hemi-ellipsoidal) is represented by a triangular mesh. Reaction and diffusion are computed in elements defined by all the triangles surrounding each vertex, or node. Growth occurs by movement of nodes normal to the surface, according to the concentration of the growth catalyst (X) on the node. When any original triangle (heavy lines) has grown such that a side is twice its original length, a new triangle (light lines) is inserted inside it, in order to maintain accuracy. On boundaries between regions with new triangles (fast growth) and old triangles (slow growth), one-way connections (dashed lines B → C) are made, so that a node never has more than six neighbours.