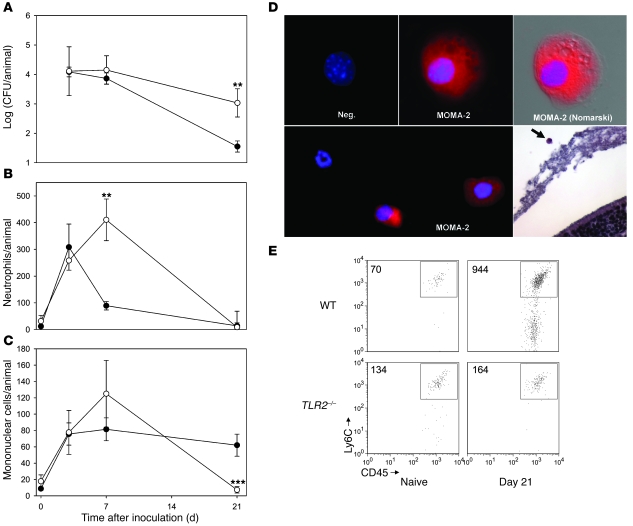
Figure 1. Macrophages are recruited to nasopharynx in association with clearance of pneumococcal isolate P1121, and responses are attenuated in the absence of TLR2 signaling.
Upper respiratory tract lavages were analyzed at the time indicated following i.n. inoculation of C57BL/6 WT mice (filled symbols) and congenic Tlr2–/– mice (open symbols) for quantitative culture to determine the time course of P1121 colonization (A). Cells in cytospin preparations of colonized mice were used to determine the time course of (B) neutrophil and (C) mononuclear cell recruitment. Animals at day 0 were mock colonized. n = 5 to 20 mice per group per time point. Values represent means ± SEM. (D) MOMA-2–positive mononuclear cells are recruited to the lumen of the nasopharynx. MOMA-2 mAb staining (red) of mononuclear cells in the cytospin preparations of nasal lavages from mice 7 days after P1121 challenge with or without Nomarski optics. Isotype-matched antibody was used as a negative control (Neg.). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Lower right panel shows a mononuclear cell (arrow) and olfactory epithelium lining the nasal cavity in a tissue section stained with H&E. Original magnification, ×1000 (upper panels); ×400 (lower left panel); ×200 (lower right panel). (E) Quantification by flow cytometry showing a representative experiment comparing the number of infiltrating macrophages in pooled nasal lavages from 5 WT or Tlr2–/– mice at day 21 of P1121 colonization. Naive mice were mock inoculated with PBS. The numbers in the upper left corners indicate the number of Ly6C+ and CD45+–double-positive cells in the sample. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.