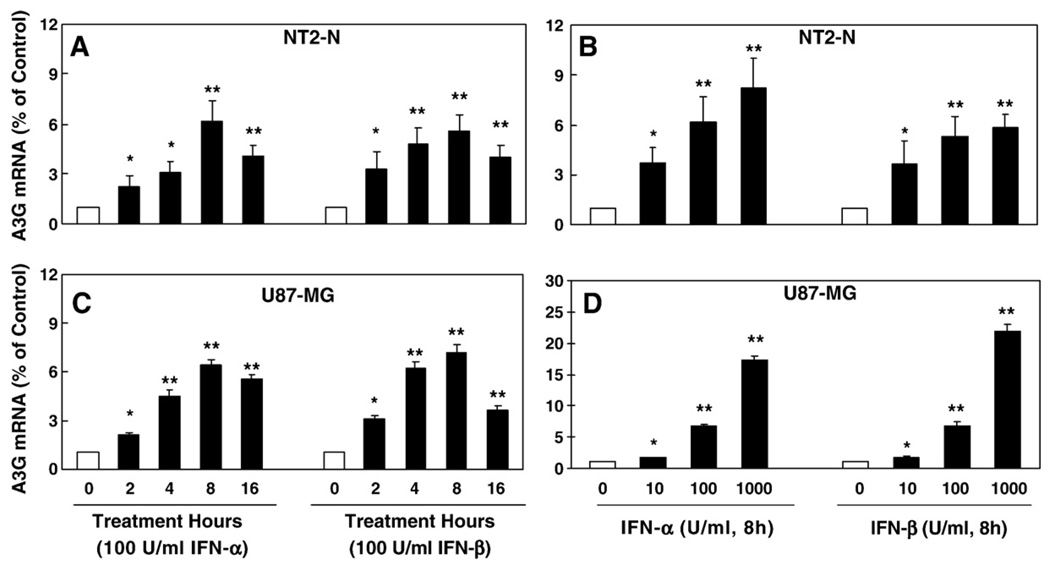
Fig. 3.
Effect of IFN-α and IFN-β on APOBEC3G expression in NT2-N cells and U87-MG cells. (A) Time-course effect of IFN-α and IFN-β on APOBEC3G mRNA expression. The NT2-N cells were treated with IFN-α or IFN-β for the indicated time points. (B) Dose-dependent effect of IFN-α and IFN-β on APOBEC3G expression. The NT2-N cells were treated with IFN-α or IFN-β at indicated concentrations for 8 h. (C) Time-course effect of IFN-α and IFN-β on APOBEC3G mRNA expression. The U87-MG cells were treated with IFN-α or IFN-β for the indicated time points. (D) Dose-dependent effect of IFN-α and IFN-β on APOBEC3G expression. The U87-MG were treated with IFN-α or IFN-β at indicated concentrations for 8 h. For the data shown in A, B, C and D, APOBEC3G mRNA levels were analyzed by the real-time RT-PCR and were expressed as fold increase over untreated NT2-N cells or U87-MG cells (defined as 1). The data shown in A, B, C, and D is expressed as mean±SD of triplicate cultures, representative of three independent experiments (*, p<0.01; **, p<0.001; treated by IFN-α or IFN-β vs. untreated).