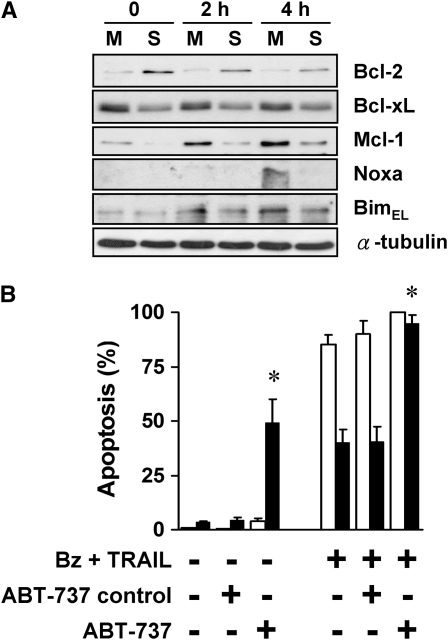
Figure 5.
Balance of anti- and proapoptotic proteins and response to treatment is altered in spheroids, contributing to apoptotic resistance. (A) Expression of Bcl-2 increases and Mcl-1 decreases when A549 cells form spheroids. A panel of anti- and proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins were screened by immunoblot in A549 monolayers (M) and spheroids (S), before and after treatment with 100 nM bortezomib plus 1 ng/ml TRAIL for 2 and 4 hours. Bcl-2 was up-regulated after A549 spheroids formed spheroids, whereas Bcl-xL and Mcl-1 were down-regulated. At 4 hours after treatment, there was a significant up-regulation of Noxa in monolayers, but not in spheroids. (B) ABT-737, a BH3 mimetic that blocks Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Bcl-w, induces apoptosis in spheroids and eliminates apoptotic resistance. At baseline, the Bcl-2 family inhibitor, ABT-737, alone (10 μM) induced apoptosis in A549 spheroids without any effect on monolayers. After exposure to bortezomib plus TRAIL, 10 μM ABT-737 induced a significant increase in apoptosis of spheroids, so that the response to treatment was equal in monolayers (open bars) and spheroids (solid bars). The negative control enantiomer of ABT had no effect (*different from negative control for ABT; mean ± SD; n = 3; P < 0.01).