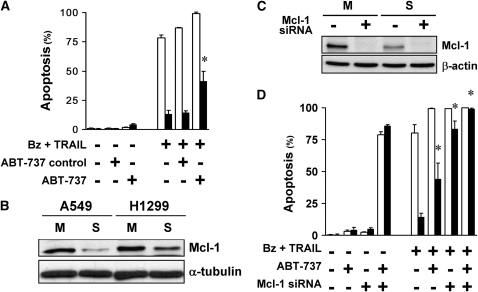
Figure 7.
Bcl-2 family proteins contribute to the multicellular resistance of H1299 spheroids. (A) ABT-737 alone did not eliminate the multicellular resistance of spheroids. At baseline, the Bcl-2 family inhibitor, ABT-737, alone (10 μM) had no effect in H1299 monolayers (open bars) and spheroids (solid bars). After exposure to bortezomib plus TRAIL, 10 μM ABT-737 induced an increase in apoptosis of spheroids, but did not eliminate the multicellular resistance. The negative control enantiomer of ABT had no effect (*different from negative control for ABT; mean ± SD; n = 3; P < 0.01). (B) H1299 spheroids have higher expression level of Mcl-1 than A549 spheroids. By immunoblot, Mcl-1 was down-regulated in spheroids (S) compared with monolayers (M) in both A549 and H1299 cells. However, H1299 spheroids retained higher expression levels of Mcl-1 than A549 spheroids. (C) Mcl-1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) depletes the expression of Mcl-1 in H1299 monolayers and spheroids. Mcl-1 was depleted by siRNA, as measured at 48 hours after transfection, the time when apoptotic agents were added. (D) Depletion of Mcl-1 largely removes multicellular resistance in H1299 spheroids. Depletion of Mcl-1 by itself did not induce apoptosis in H1299 monolayers (open bars) and spheroids (solid bars), but significantly removed the multicellular resistance of H1299 spheroids to 100 nM bortezomib (Bz) plus 1 ng/ml TRAIL treatment for 24 hours. ABT-737 (10 μM) exposure plus Mcl-1 depletion induced death of monolayers and spheroids, and removed all multicellular resistance to bortezomib plus TRAIL (*different from spheroids treated with bortezomib plus TRAIL; mean ± SD; n = 3; P < 0.01).