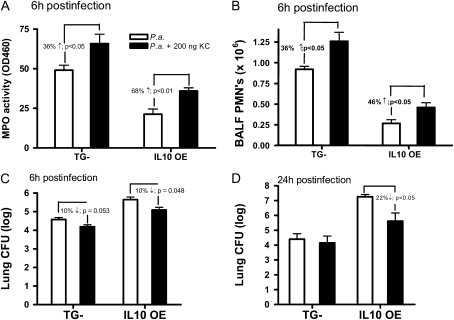
Figure 6.
Coadministration of KC with P. aeruginosa increased PMN recruitment and enhanced bacterial clearance. In (A)–(C), mice were given an intratracheal infection with P. aeruginosa at a dose of 0.8 × 106 CFU with or without the coadministration of 200 ng KC. (A) Lung MPO activity measured 6 hours after administration of bacteria. (B) BALFs were collected at 6 hours, and PMN values determined from total number of leukocytes (Coulter counted) multiplied by the percent neutrophils determined by differential counts on cytospin samples. (C ) Lung CFU determination 6 hours after infection. (D) Mice were given an intratracheal infection of 1.0 × 106 CFU of P. aeruginosa with or without KC. Lung CFU were measured at 24 hours after infection. Data are means (±SEM), and are representative of two independent experiments, with n = 7–8 mice/group.