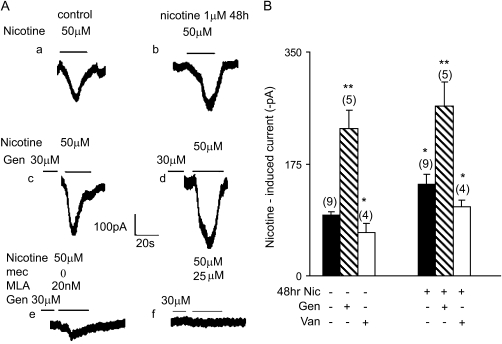
Figure 4.
Effect of chronic nicotine exposure and genistein on nicotine-induced currents in BECs. (A, a) The inward current induced by 50 μM nicotine in a control cell. (A, b) A 48-hour incubation with 1 μM nicotine increased the inward current induced by 50 μM nicotine roughly 26% compared with control. (A, c) The inward current induced by 50 μM nicotine was increased roughly 58% by preincubation with genistein (30 μM) for 2 hours. (A, d) The combination of 48-hour incubation with 1 μM nicotine (50 μM) and 2-hour preincubation with genistein (30 μM) further increased nicotine-induced inward current. (B) Mean effects of inhibition of kinase and phosphatase activity by genistein and vanadate, respectively, on nicotine (50 μM)-induced current. Cells were incubated in control media or media containing 1 μM nicotine for 48 hours. Cells were then incubated for 2 hours with 30 μM genistein or 1 hour with 20 μM vanadate, as shown. Genistein (30 μM) enhanced both acute and chronic nicotine–induced currents, whereas 20 μM vanadate decreased both acute and chronic nicotine-induced currents. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of cells averaged (mean ± SEM; * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01).