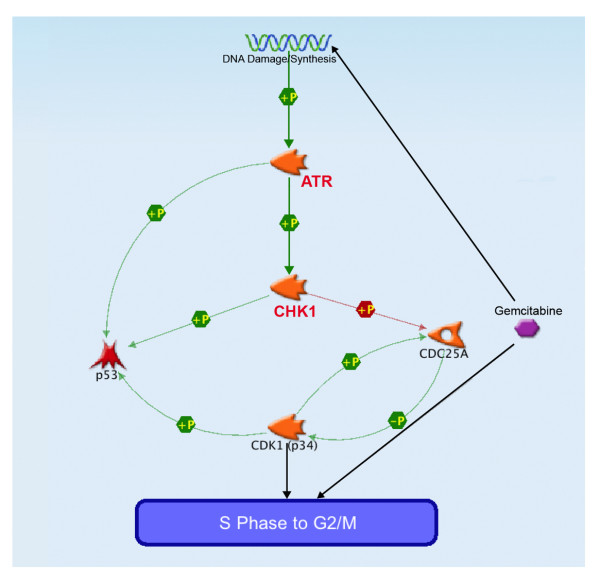
Figure 6.
Schematic of the role of CHK1 and ATR in sensitization to gemcitabine. Genes identified as synergistic to gemcitabine in the RNAi kinase screens are shown in red. Gemcitabine induced DNA damage results in the phosphorylation and activation of serine/threonine-protein kinase CHK1 by ATR. The activated CHK1 then phosphorylates Cdc25A, leading to cell cycle arrest in G2/M. This rapid response via CHK – Cdc25A pathways additionally is followed by the p53-mediated maintenance of G1/S arrest. Tumor suppressor p53 plays a key role in the G2/M checkpoint arrest as well. In the maintenance stage, ATR phosphorylates Ser15 of p53 directly and Ser20 through activation of CHK1. Phosphorylated p53 activates its target genes, including cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21), which binds to cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2) and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4). Map was constructed with MapEditor (GeneGO).