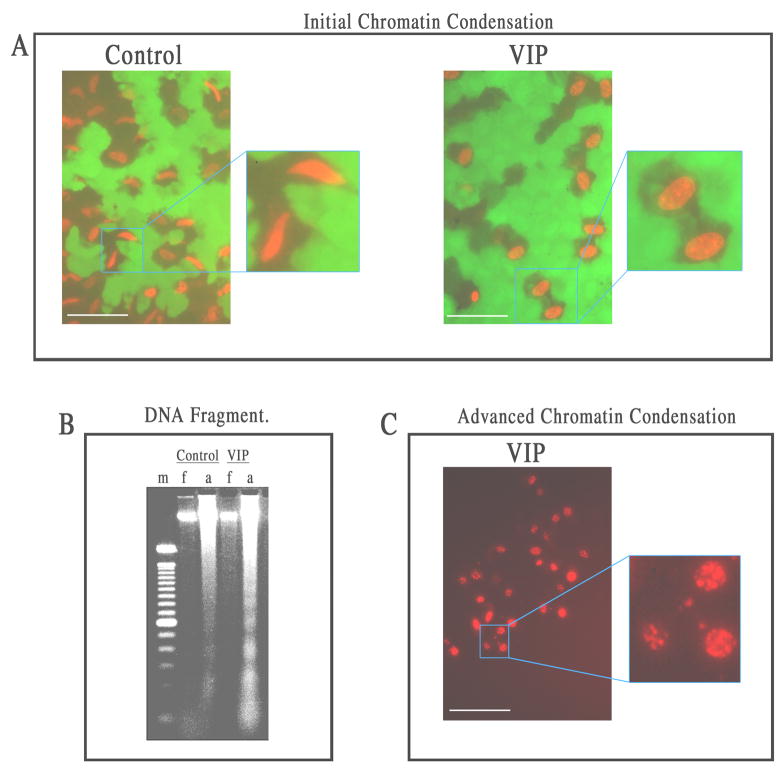
Fig. 3.
Features of nuclear apoptosis in VIP (10−6 M)-pretreated CE cells dying of severe oxidative stress: (A) initial peripheral chromatin condensation, (B) genomic DNA fragmentation,(C) advanced chromatin condensation. White bar length=15 μm. For A: Fluorescence microscopy of flat-mounted corneoscleral explants in a live and dead cytotoxicity test of CE cells after a 17 h-exposure to H2O2. In the control corneal cups, CE cells dying of necrosis displayed spindle-shaped nuclei, while those in VIP-pretreated corneal cups displayed chromatin condensation at the periphery of the nuclei. For B: Agarose gel electrophoresis showing ladder formation by fragmented genomic DNA isolated from CE cells that remained attached (a) to VIP-pretreated, but not control corneal cups. No DNA fragmentation was observed in CE cells that detached from the corneas and became free-floating (f) in either the control or VIP-pretreated corneal cups. m: marker (100-bp DNA ladder). For C: Fluorescence microscopy of a flat-mounted corneoscleral explant in a live and dead cytotoxicity test showing advanced chromatin condensation in CE cells in VIP-pretreated corneal cups after a 27 h-exposure to H2O2, followed by a 26 h-recovery in the semi-complete medium.