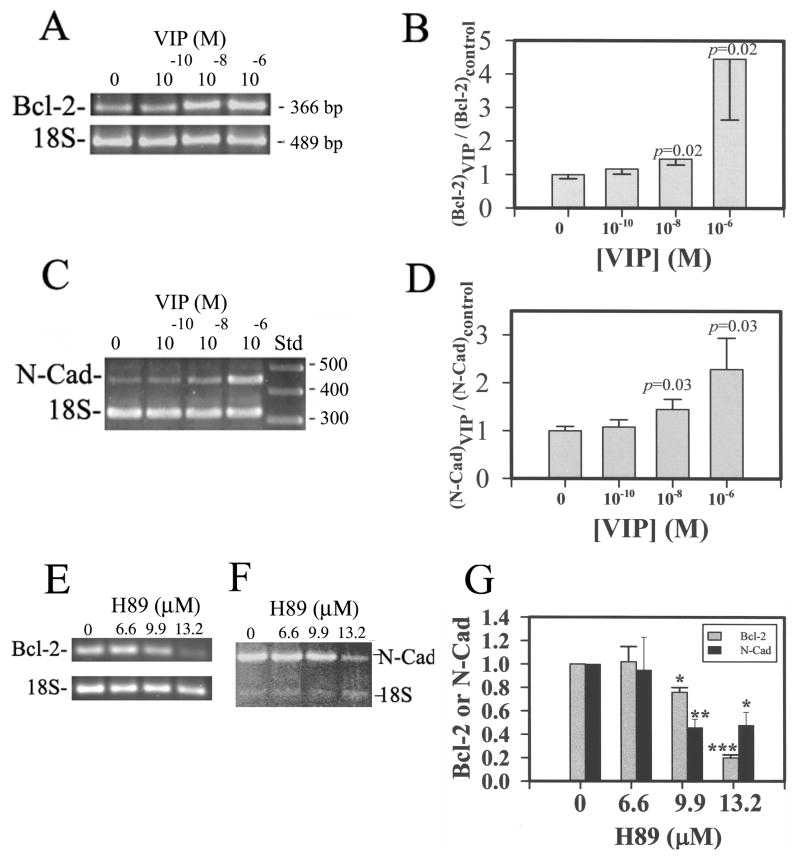
Fig 8.
Bcl-2 and N-cadherin mRNA levels in oxidative stress-injured CE cells increased by VIP pre-treatment in VIP concentration-dependent and protein kinase A inhibitor (H89)-sensitive manners. (A & C) Electrophoresed (2% agarose) semi-quantitative RT-PCR products showing the VIP concentration-dependency of Bcl-2 mRNA (A) and N-cadherin mRNA (C). (B& D) The ratio of normalized CE cell Bcl-2 (B) and N-cadherin (D) cDNA (against the 18S internal standard) levels over that averaged from the control CE cells of the same experiment (Y-axis) was shown as a function of VIP concentration. Data were combined from four separate experiments. (E & F) The protein kinase A inhibitor H89 attenuated the effect of 10−8 M VIP pre-treatment on up-regulation of Bcl-2 (E) and N-cadherin mRNA (F) levels. (G) The relative levels of Bcl-2 and N-cadherin in 10−8 M VIP-treated CE cells decreased by H89. The data were averaged from three experiments. For B: The difference of the control vs VIP-pre-treated was significant at P =0.02 for both 10−8 and 10−6 M-VIP-pre-treated CE cells in corneoscleral explants. The difference among various groups of corneoscleral explants with CE cells pre-treated with 0 (N=12), 10−10 (N=10), 10−8 (N=10), and 10−6 (N=9) M VIP was significant (P = 0.018, ANOVA). For D: The difference of the control vs VIP-pre-treated was significant at P =0.03 for both 10−8 and 10−6 M VIP-pre-treated CE cells in corneoscleral explants. The difference among various groups of corneoscleral explants treated with 0 (N=9), 10−10 (N=8), 10−8 (N=8), and 10−6 (N=8) M VIP was significant (P = 0.049, ANOVA). For G: The difference of the control vs H89-pre-treated was significant at P =0.001 (*), p=0.0001 (**), p<0.0001 (***). The difference in Bcl-2 levels among various groups of corneoscleral explants treated with 0 (N=4), 6.6 (N=2), 9.9 (N=4), and 13.2 (N=3) μM H89 was significant (P <0.0001, ANOVA). The difference in N-Cadherin levels among various groups of corneoscleral explants treated with 0 (N=4), 6.6 (N=2), 9.9 (N=3), and 13.2 (N=4) μM H89 was significant (P =0.06, ANOVA).