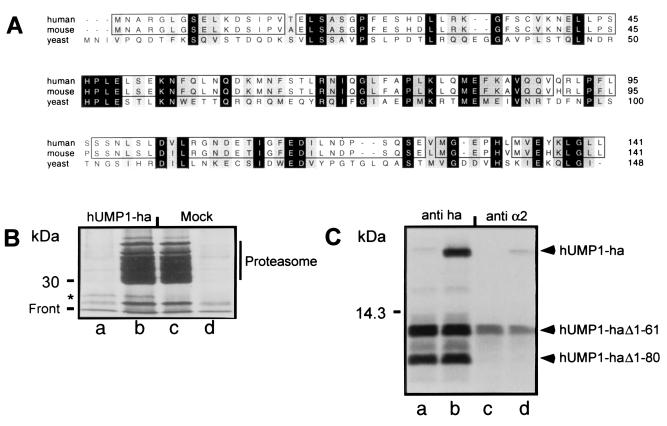
Figure 1.
Identification of human and mouse homologue of the yeast Ump1p protein and its interaction with mammalian proteasome. (A) CLUSTALW sequences of human and mouse protein are aligned with yeast Ump1p. Identical amino acids are labeled in black, and similar amino acids are labeled in gray. Identical amino acids between human and mouse are boxed. (B) 293T cells were transiently transfected with recombinant plasmid directing the synthesis of hUMP1-ha (lanes a and b) or mock transfected (lanes c and d) and labeled after 24 h with [35S]methionine/cysteine. Cells were then solubilized, and cleared lysate was immunoprecipitated either with a monoclonal antibody against the ha epitope (lanes a and d) or with a polyclonal antibody against the proteasome (lanes b and c). The position of hUMP1-ha is indicated by an asterisk. (C) Fragments generated from internal initiation sites were used to identify the region of hUMP1-ha important for interaction with the proteasome. The cDNA encoding the wild-type hUMP1-ha (lanes b and d) or a mutant lacking the first initiation codon (lanes a and c) was transcribed and translated in vitro. Samples were immunoprecipitated either with the anti-ha antibody (lanes a and b) or with MCP21 (lanes c and d). The positions of full-length and truncated hUMP1-ha are indicated.