Figure 3. Selective metabolism of extracellular glutamate prevents soluble Aβ facilitated-LTD.
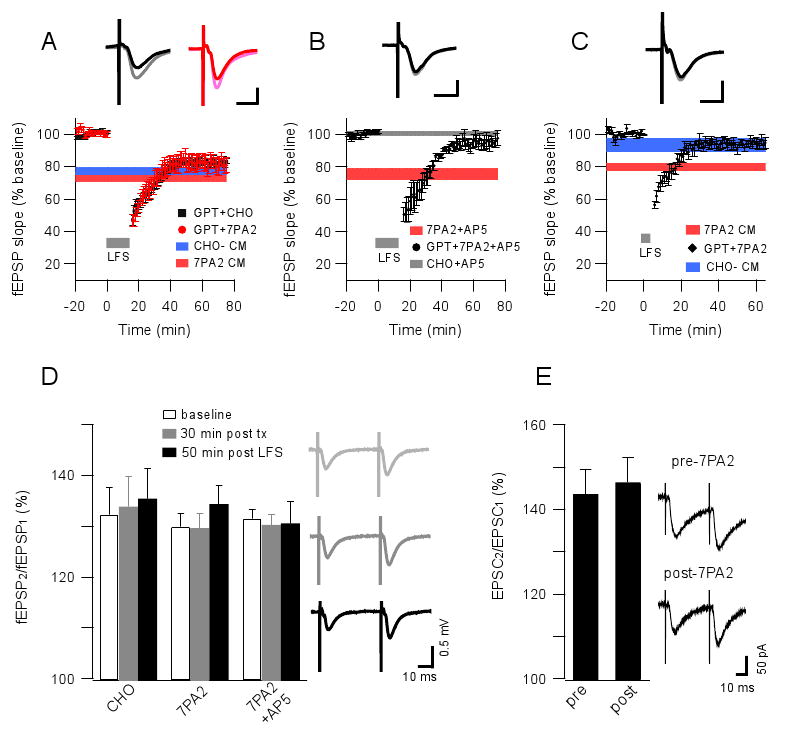
(A) A glutamate scavenger system (glutamic pyruvic transaminase [GPT, 5 unit/ml] + pyruvate [2 mM]) has no significant effect on the fEPSP baseline and 900-pulse LTD in CHO- or 7PA2 CM treated slices. Horizontal colored bars represent the corresponding means ± SEMs from Fig.1C. Insets in A-C represent typical fEPSPs recorded before (light) and 50 min after (dark) LFS; horizontal calibration bar, 10 ms; vertical bar, 0.5 mV. (B) 900-pulse LTD (grey bar) was blocked by AP5 (50 μM) in slices exposed to GPT + pyruvate for 15 min prior to 7PA2 CM (n=6). Red horizontal bar shows the LTD resistant to the same dose of AP5 in the absence of exposure to scavengers. (C) 300-pulse LTD (grey bar) was significantly prevented by co-administering glutamate scavengers with the 7PA2 CM. Horizontal colored bars represent the corresponding means ± SEMs from Fig.1B. (D) Paired-pulse facilitation in slices exposed to 7PA2 CM, CHO- CM or 7PA2 CM + AP5 (50 μM) measured before (white) or 30 min after (grey) adding these media or else measured 50 min after (black) a 900-pulse induction of LTD. At right are typical traces of these field recordings from the 7PA2 group. (E) Similar paired-pulse facilitation recorded by whole-cell voltage clamping at -70 mV in CA1 pyramid cells before and 30 min after 7PA2 CM exposure. At right are typical traces. Data are means ± SEMs.
