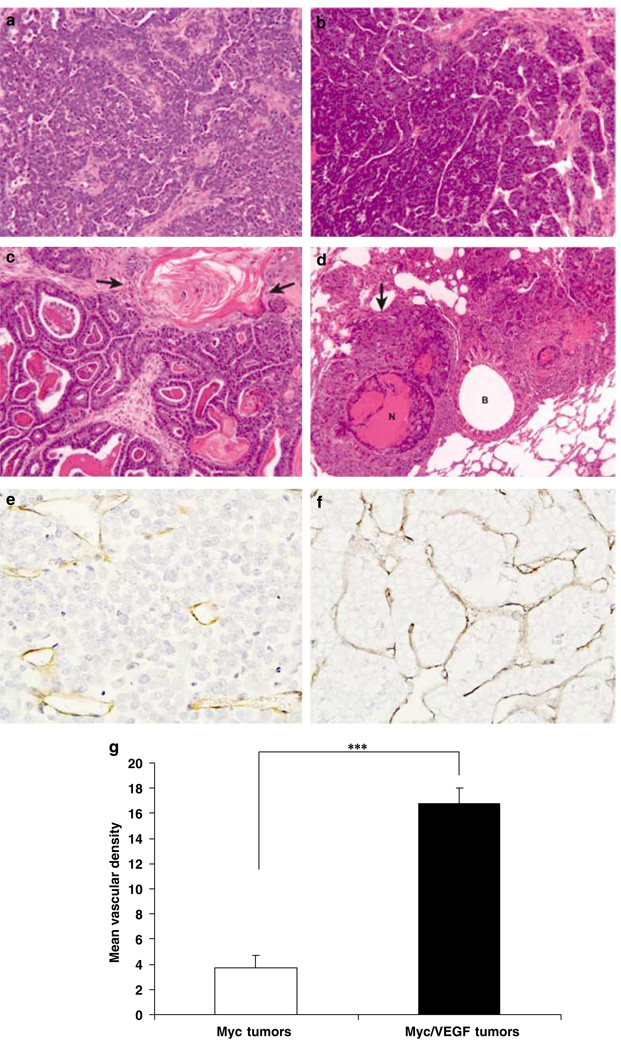
Figure 1.
Morphology of primary Myc and Myc/VEGF mammary tumors. (a) Adenocarcinoma of a Myc transgenic mouse. (b) Adenocarcinoma of a Myc/VEGF mouse. (c) Adenosquamous (metaplastic) carcinoma of a Myc/VEGF mouse. Arrows indicate stratified squamous epithelium with keratinization. (d) Large pulmonary metastasis (arrow) with central necrosis (N). Metastasis surrounds a bronchus (B). (e) Immunostaining for CD-31 in a Myc tumor. (f) Myc/VEGF tumor showing higher vascularization (anti-CD-31 staining) than Myc tumors. (g) Comparison of the mean vascular density between Myc and Myc/VEGF tumors. ***P < 0.0004.