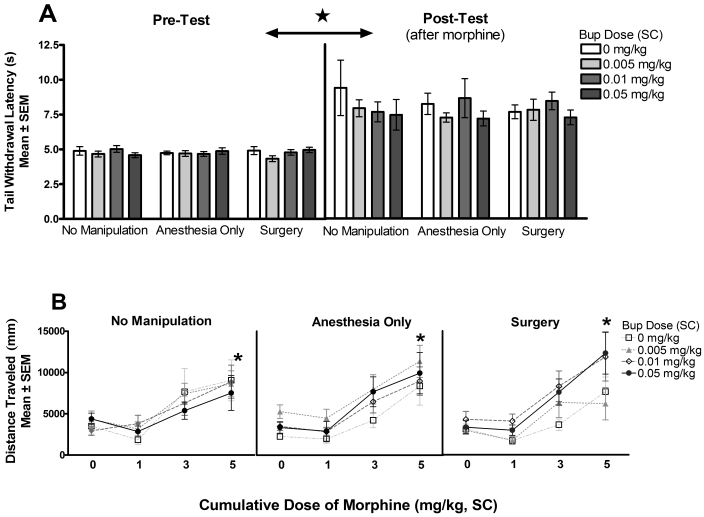
Figure 4.
(A) Experiment 1—analgesic effects of morphine (tail-withdrawal latency). Sensitivity to the analgesic effects of morphine was tested 9 to 10 d after postoperative buprenorphine (Bup) administration. Neither surgery nor any of the postoperative doses of buprenorphine induced lasting changes in subsequent exposure to the analgesic effects of morphine. *Morphine induced a significant (P < 0.05) increase in tail-withdrawal latency. (B) Experiment 1—locomotor effects of morphine (locomotor testing). Sensitivity to the locomotor effects of morphine was tested 9 to 10 d after postoperative buprenorphine administration. Neither surgery nor any of the postoperative doses of buprenorphine induced lasting changes in subsequent exposure to the locomotor-stimulating effects of morphine. *, Morphine induced a significant (P < 0.05) increase in locomotor activity.