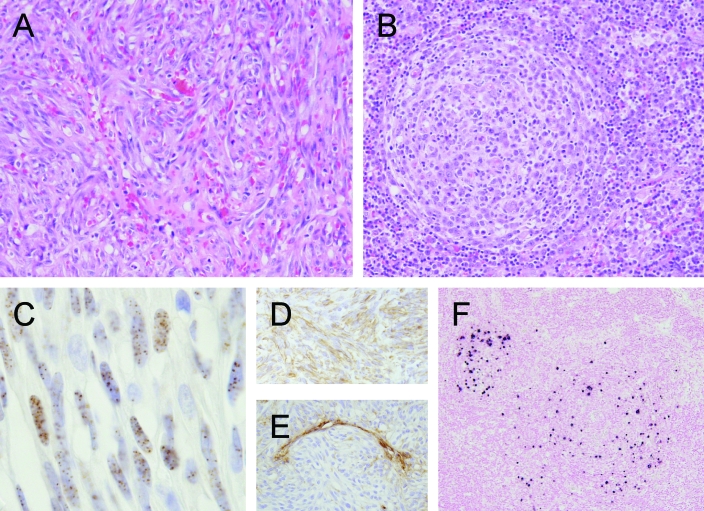
Figure 1.
Pathology of KSHV infection of humans. (A) Kaposi sarcoma (KS) and (B) multicentric Castleman disease (MCD) are associated with KSHV infection in immunocompromised and normal humans. KS is characterized by bundles of spindeloid cells forming fascicles and irregular channels containing erythrocytes. These spindeloid cells (C) may stain positively for latent nuclear antigen, (D) are vimentin-positive, and (E) often are negative for von Willebrand factor VII. MCD is a lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by generalized follicular lymphadenopathy with accumulation of plasma cells and proliferation of blood vessels within germinal centers (B). (F) Nucleic acid may be localized to the mantle region of affected follicles by means of in situ hybridization.