Figure 1. DGR Homing Occurs through an RNA Intermediate.
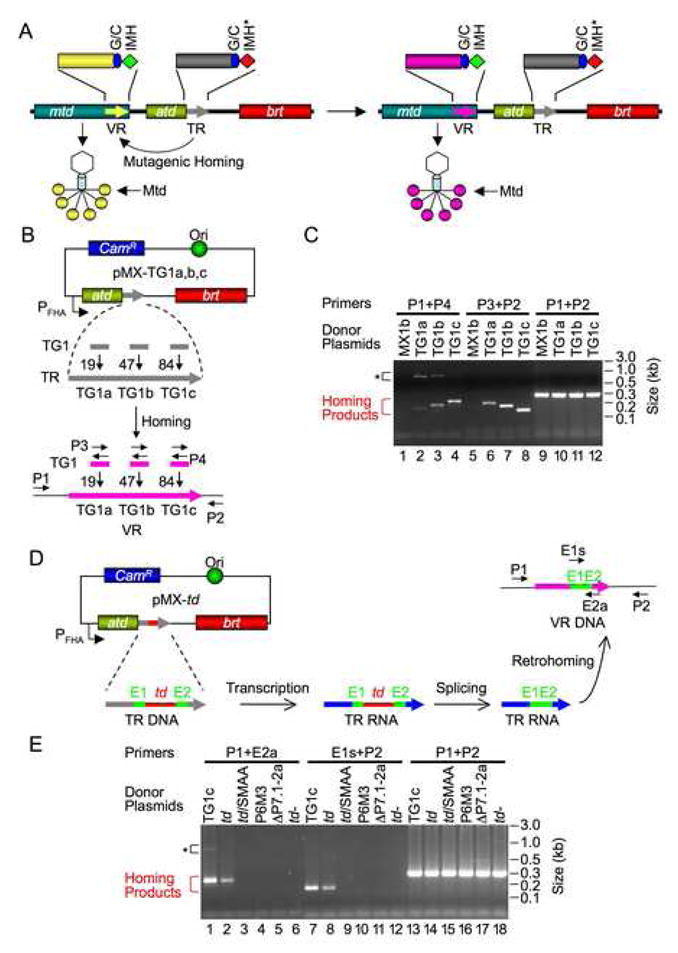
(A) Bordetella phage DGR cassette undergoes mutagenic homing and facilitates tropism switching. mtd, atd, brt and the two repeats (VR and TR) are indicated. VR and TR are expanded to show the (G/C)14, IMH and IMH* elements. DGR homing leads to VR diversification, resulting in progeny phages with altered Mtd trimers at the distal ends of tail fibers.
(B) PCR-based DGR homing assays. Plasmids pMX-TG1a, b, c are derived from pMX1b, which carries the BPP-1 atd-TR-brt region placed downstream of the BvgAS-regulated fhaB promoter. pMX-TG1a, b, c contain 36 bp inserts (TG1), corresponding to ligated exons of the T4 td group I intron flanked by SalI sites, at TR positions 19 (TG1a), 47 (TG1b) or 84 (TG1c), respectively. Grey and pink arrows represent TR and VR, respectively. Small horizontal arrows indicate primers used for homing assays: P1, sense-strand primer located in mtd; P2, antisense-strand primer downstream of VR; P3 and P4 are sense- and antisense-strand primers, respectively, that anneal to ligated td exons. CamR, chloramphenicol resistance gene.
(C) pMX-TG1a, b, c are functional donors for DGR homing. Assays were performed following BPP-1d single-cycle lytic infection of B. bronchiseptica RB50 cells transformed with the indicated donor plasmids. pMX1b (negative control) lacks the TG1 insert. Larger PCR products (*) in lanes 2–4 are Brt-independent PCR artifacts (Figure 3, lanes 1&2 and data not shown). They contain sequences from mtd to TR, have not undergone adenine mutagenesis, and were likely generated by PCR template switching between BPP-1d DNA and contaminating donor plasmids in phage DNA preparations. P1+P2 product levels demonstrate that approximately equal amounts of input DNA were used for PCR homing assays.
(D) Testing the DGR retrohoming hypothesis. The T4 td group I intron (td) and flanking exons (E1, E2) were inserted at position 84 in TR. Following transcription and intron splicing, ligated exons will be retained in a subset of TR-containing transcripts. If homing occurs via an RNA intermediate (retrohoming), some VRs will acquire ligated exons. Primers used for PCR homing assays are indicated by small horizontal arrows: P1 and P2 are described in (B); E1s, sense-strand primer annealing to E1; E2a, antisense-strand primer annealing to E2.
(E) Precisely ligated td exons are transferred to VR during homing. Products from PCR homing assays with indicated primer pairs and donor plasmids are shown. TG1c, pMX-TG1c positive control; td, pMX-td donor plasmid; td/SMAA, RT-deficient pMX-td derivative; P6M3 and ΔP7.1-2a, splicing-defective pMX-td derivatives; td-, pMX1b with the td intron and flanking exons inserted in inverted orientation at TR position 84. *, Brt-independent PCR artifacts.
