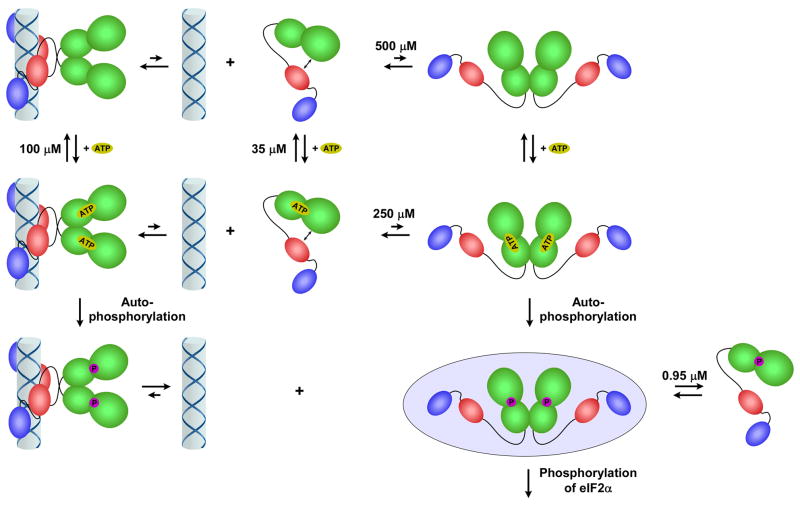
Figure 3.
Model for PKR activation. PKR exists in an open conformation (i) in a weak monomer-dimer equilibrium. Dimerization is induced by binding to dsRNA (ii) or at high protein concentration (iii), producing an enzyme form competent to undergo autophosphorylation. ATP is able to bind readily to both monomeric and dimeric PKR. The autophosphorylated dimer dissociates readily from dsRNA (iv). The PKR dimer is stabilized by phosphorylation (v) and represents the enzyme form competent to phosphorylate eIF2α. The PKR dimerization dissociation constants were obtained from reference [24] and the ATP dissociation constants were obtained from reference [22].