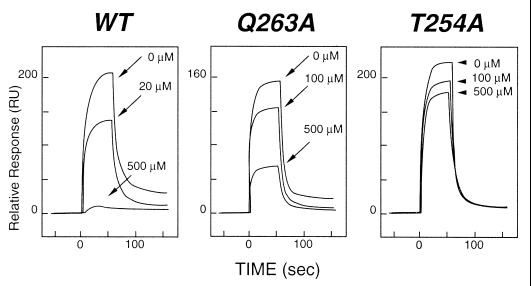
Figure 4.
Inhibition of TRAF3 binding to CD40 by synthetic peptides. Binding was measured by using surface plasmon resonance with a BIACORE 3000 instrument (Biacore AB, Uppsala). A recombinant fragment representing the entire cytoplasmic domain of CD40 was cloned as a glutathione S-transferase fusion protein, expressed in Escherichia coli, and purified by affinity chromatography on a glutathione-Sepharose (Amersham Pharmacia) column. The fusion partner was removed by thrombin digestion, and the CD40 fragment was purified by ion-exchange chromatography. The CD40 domain was immobilized on a Biacore CM5 sensor chip, and the TRAF3 TRAF domain was injected at 3.5 μM. The Left sensorgram shows the relative response for binding interactions between immobilized CD40 and TRAF3 and inhibition of this binding by a synthetic peptide from the cytoplasmic domain of CD40 (250PVQETLHGCQPVTQEDG266). A series of peptides with alanine substituted singly for each residue in the fragment was tested for inhibition of binding of TRAF3 to CD40. Mutant peptides were injected at concentrations ranging from 20 to 500 μM. As can be seen from the Center and Right sensorgrams, striking changes in inhibition were observed when alanine was substituted for Q263 or T254, suggesting reduced binding of the mutant fragments. Substitution of alanine for other residues in the peptide did not significantly alter levels of inhibition observed with the wild-type (WT) peptide.