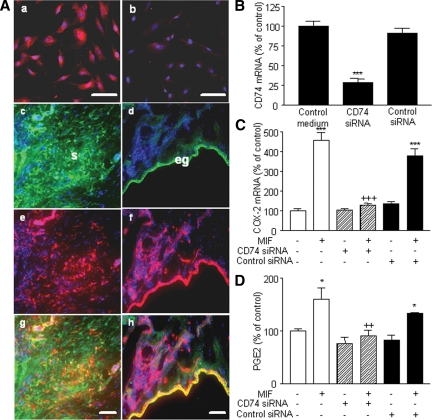
Figure 4.
Detection of CD74 in endometriotic cells and effect of CD74 knockdown on COX-2 expression and PGE2 secretion. CD74 was immunostained in endometriotic stromal cell culture (A) as described in Materials and Methods. CD74 was detectable in endometriotic cells using a specific monoclonal mouse antibody (a), whereas a weak immunostaining was observed in cells incubated with isotype control mouse IgG (b). A, CD74, vimentin, and cytokeratin-8 were immunostained in ectopic endometrial tissue as described in Materials and Methods, and DAPI (blue) was used for counterstaining. Note the green fluorescence corresponding to vimentin (c) or cytokeratin-8 (d) and the red fluorescence corresponding to CD74 (e and f). Superposition of the green and red signals shows simultaneous immunostaining between CD74 and vimentin (g) and CD74 and cytokeratin-8 (h); eg, Epithelial gland; s, stroma. Scale bar, 50 μm. Endometriotic stromal cells were transfected with 33 nm CD74 siRNA or negative control siRNA for 48 h and then incubated or not with 50 ng/ml MIF for 24 h. After total RNA extraction and RT, CD74 and COX-2 mRNA levels were quantified by quantitative real-time PCR, and PGE2 secretion was measured in the culture supernatants using EIA. CD74 siRNA significantly inhibited CD74 mRNA expression (B), and prevented MIF stimulation of COX-2 mRNA expression (C) and PGE2 secretion (D). Data are from three different endometriotic cells cultures (patient nos. 2, 8, and 11, Table 1). *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001 vs. control medium using ANOVA and the Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test post hoc. ++, P < 0.01; +++, P < 0.001 are significantly different from cells incubated with the same concentration of MIF, using ANOVA and the Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test post hoc.