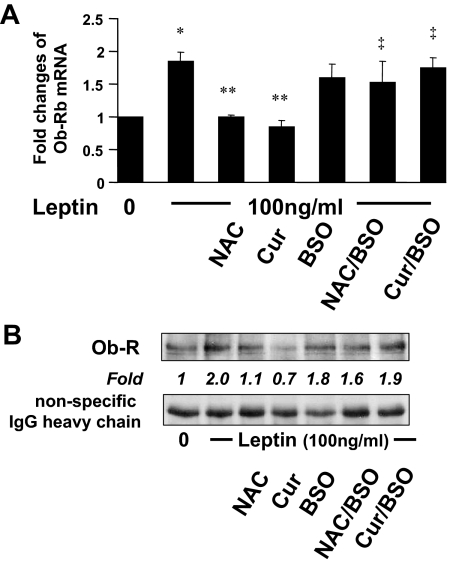
Figure 5.
The depletion of cellular GSH by BSO eliminates the suppressive effect of curcumin (Cur) on gene expression of Ob-R in activated HSCs in vitro. Serum-starved HSCs were divided into two groups. In one group, cells were stimulated with or without leptin (100 ng/ml) plus curcumin (20 μm) or NAC (5 mm) in serum-free media for 24 h. In the other group, cells were pretreated with BSO (0.25 mm) for 1 h before the addition of leptin (100 ng/ml) plus curcumin (20 μm) or NAC (5 mm) in serum-free media for an additional 24 h. Total RNA or whole cell extracts were prepared. A, Real-time PCR analyses of Ob-R mRNA (n = 3). *, P < 0.05 vs. the untreated control (first column); **, P < 0.05 vs. cells treated with leptin only (second column); ‡, P < 0.05, vs. cells treated with leptin plus NAC or curcumin (third or fourth column, respectively). B, Western blotting analyses of immunoprecipitated Ob-R. Representatives were from three independent experiments. Italic numbers were fold changes in densities of the bands compared with the untreated cells (first well) after normalization with nonspecifically recognized heavy chain of IgG (n = 3).