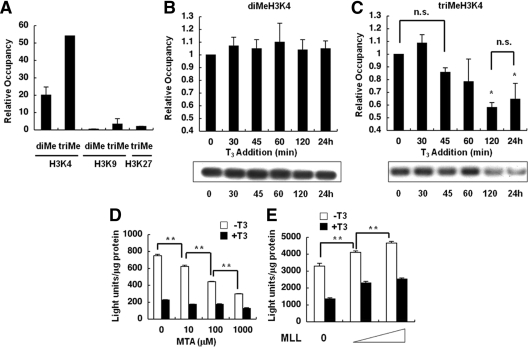
Figure 2.
Histone methylation at H3K4, -K9, and -K27 on the TRH gene and effects of MTA and MLL. ChIP assays were performed with cells expressing the TRH promoter and the WT TR. A, ChIP assays revealed significant di- and trimethylation of H3K4 but no methylation of H3K9 and H3K27, at the basal level of the TRH gene. Values were expressed as a percentage of the input. B and C, Incubation with 100 nm T3 for longer than 2 h induced a significant reduction in the trimethylation of H3K4 (C) but no change in the level of dimethylation (B). Each level was compared with the basal level (0 min). Representative results of ChIP assays are demonstrated. D, Luc assays in GH4C1 cells stably expressing the TRH promoter and the WT TR in the absence or presence of 100 nm T3 demonstrated that treatment with 10 μm to 1.0 mm MTA inhibited the basal promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner. E, GH4C1 cells were transiently transfected with the TRH-Luc reporter gene, WT TR, and MLL. Overexpression of MLL caused a significant increase in the basal promoter activity of the TRH gene in a dose-dependent manner. The data are presented as the mean ± se for three (A–C) or six (D and E) independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 vs. 0 min (C); **, P < 0.01 (D and E). n.s., Not significant.