Fig. 1.
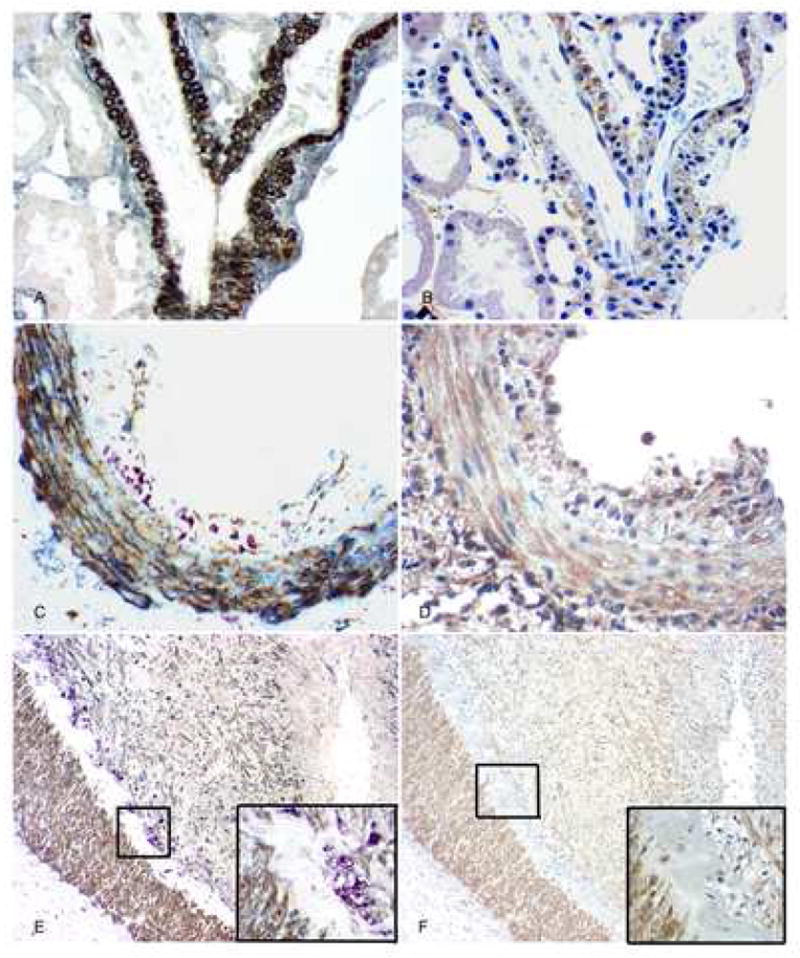
PDGF-D and PDGF-Rβ expression in arteries. A: In normal group, triple immunolabeling shows that PDGF-D (brown) is expressed in arterial medial smooth muscle cells that also express alpha-smooth muscle actin (blue-gray); no monocyte/macrophages (purple) are found. There is no expression of PDGF-D seen in the interstitium. B: In serial section of A, PDGF-Rβ (brown) is expressed in the similar distribution of PDGF-D in arterial wall, and is also expressed mildly in interstitium. C: In kidneys with AVR, triple immunolabeling shows that PDGF-D (brown) is expressed in arterial medial smooth muscle cells, some adventitial cells and some neointimal cells that also have alpha-smooth muscle actin (blue-gray) expression; It is not expressed by the subendothelial infiltrating monocyte/macrophages (purple). D: In serial section of C, PDGF-Rβ (brown) is expressed in the similar distribution of PDGF-D in the arterial wall. E: Part of an artery in kidneys with CAN, triple immunolabeling shows that PDGF-D (brown) is expressed in arterial medial smooth muscle cells and the more prominent neointimal layers compared with the other two groups, which also have alpha-smooth muscle actin (blue-gray) expression; It is not expressed by the subendothelial infiltrating monocyte/macrophages and foam cells (purple). The inset shows the framed area with high power. F and its inset: In serial section of D, PDGF-Rβ (brown) is expressed in a similar distribution of PDGF-D in the artery. Original magnification, AD, × 400, E and F, × 100.
