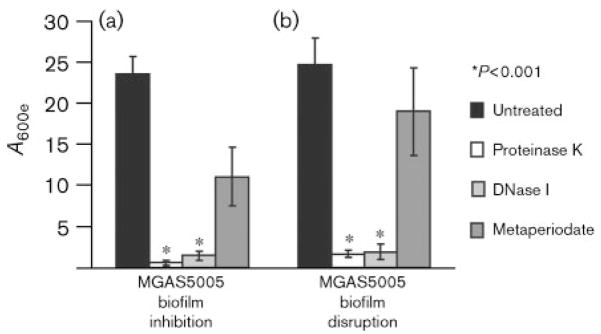
Fig. 1.
Enzymic inhibition or disruption of GAS biofilm formation. (a) To test the ability of specific enzymes to inhibit biofilm formation, proteinase K, DNase I or metaperiodate was added when the six-well plates were initially seeded with MGAS5005 in the exponential phase (OD600 0.5). After 24 h growth, strains incubated with proteinase K or DNase I produced significantly less, if any, biofilm. While metaperiodate curtailed biofilm formation, it did not abolish this ability. Each reported value is the mean±SD of at least six replicates and is adjusted by the dilution factor required to obtain a spectrophotometric reading (A600 extrapolated or A600e). (b) To test the ability of the same enzymes to disrupt an established GAS biofilm, proteinase K, DNase I or metaperiodate was added to cultures grown in six-well plates for 24 h. CV assays were completed after 1 h incubation with enzyme. Treatment with proteinase K or DNase I disrupted the biofilm and yielded a significantly reduced A600e. Treatment with metaperiodate reduced the amount of biofilm present, but was unable to completely disrupt the biofilm.