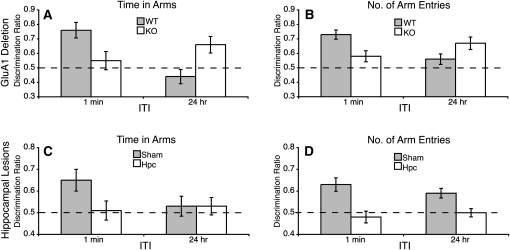
Figure 2.
Experiment 1. The effect of GluA1 gene deletion and hippocampal lesions on short-term and long-term spatial memory. Preference for the Novel arm over the familiar Other arm is shown as a discrimination ratio (Novel/Novel + Other). The dashed line indicates chance performance (0.5). (A,C) Results from the time in arms measure. (B,D) Results from the number of arm entries measure. (A,B) GluA1 gene deletion impaired preference for the Novel arm when a 1 min ITI was used, but enhanced the preference for the Novel arm when a 24 h ITI was used (wild-type mice [WT]: female, N = 12; male, N = 8; knockout mice [KO]: female, N = 8; male, N = 6). (C,D) Hippocampal lesioned mice failed to show a preference for the Novel arm at either interval (sham lesioned mice [Sham]: N = 9; hippocampal lesioned mice [Hpc]: N = 12). Error bars, ± SEM.